The Postman Rest Client is a very popular and easy to use HTTP Request composer that makes it easy to call web services, similar to Fiddler's Composer. It also provides as an alternative for autogenerating API documentation to ServiceStack's Open API support that makes it easier to call existing services but does require users to install the Postman Rest Client.
Support for Postman is built into ServiceStack and can be enabled by registering the Plugins below:
Plugins.Add(new PostmanFeature());
Plugins.Add(new CorsFeature());
INFO
As Postman makes cross-site requests, is also requires CORS support.
Once enabled, a link with appear in your metadata page:
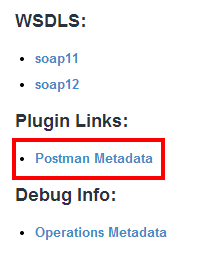
Importing the Postman Collection
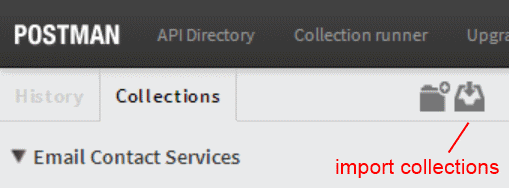
By default the link to the Postman JSON metadata collection is at /postman, this url can be imported into postman by clicking on import collections:
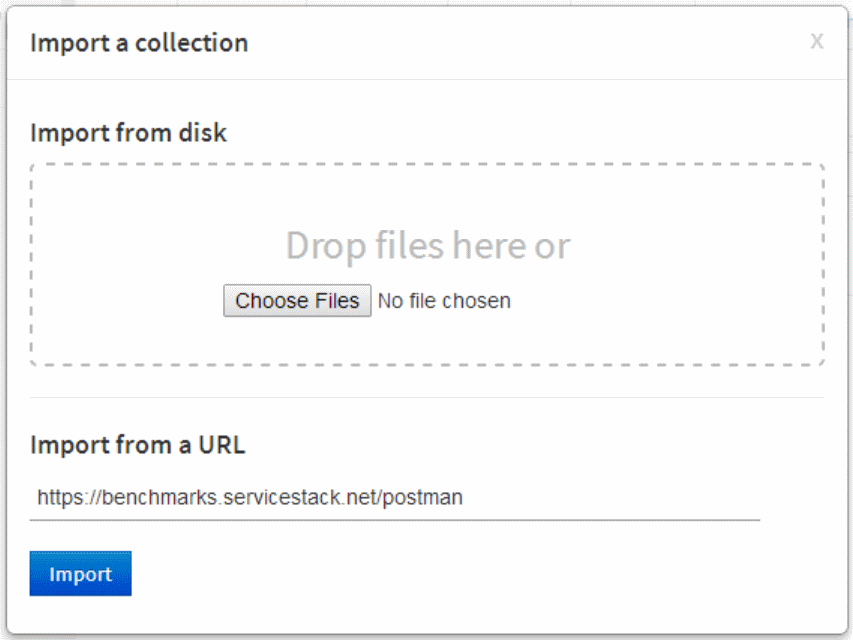
This will open up the import dialog, where you can paste the metadata url and click Import:
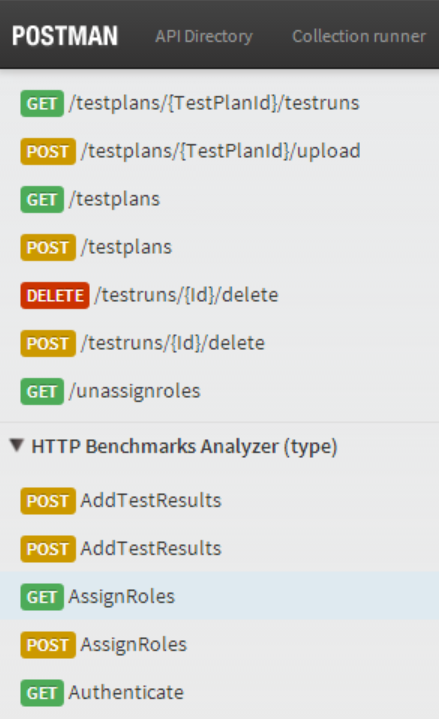
Available Routes
Once imported it will populate a list of available operations that can be selected and easily called from within the Postman UI. Just like the Open API Support the list of operations returned respects the Restriction Attributes and only shows the operations each user is allowed to see. The operations returned also favour custom user-defined routes, when none exists it will fallback to use the pre-defined routes.
Label Customization
The label for each operation can be further customized using the ?label query string param whose preferred style which can vary depending on the granularity and naming of your Request DTO's, and whether they have custom routes defined on them.
The screenshot above shows an example of importing the same service with the different label styles below:
The label param accepts a collection of string tokens that controls how the label is formatted.The type and route are special tokens that get replaced by the Request DTO name and Route respectively. Everything else are just added string literals including the + character which is just a url-encoded version of the space character.
Here are some examples using the example definition below:
[Route("/contacts/{Id}")]
public class GetContact { ... }
| /postman?label=type | GetContact |
| /postman?label=route | /contacts/{Id} |
| /postman?label=type:english | Get contact |
| /postman?label=type:english,+(,route,) | Get contact (/contacts/{Id}) |
Specifying the Default Label Format
The default label format can also be configured when registering the Postman plugin, e.g:
Plugins.Add(new PostmanFeature {
DefaultLabelFmt = new List<string> { "type:english", " ", "route" }
});
Calling Services
Calling Services is as easy as selecting the service you want to call, filling in the parameters you want to call it with then clicking Send. At a mimimum you want to specify values for all the path variables in the /pathInfo which are prefixed with a colon followed by its name, e.g: :VariableName
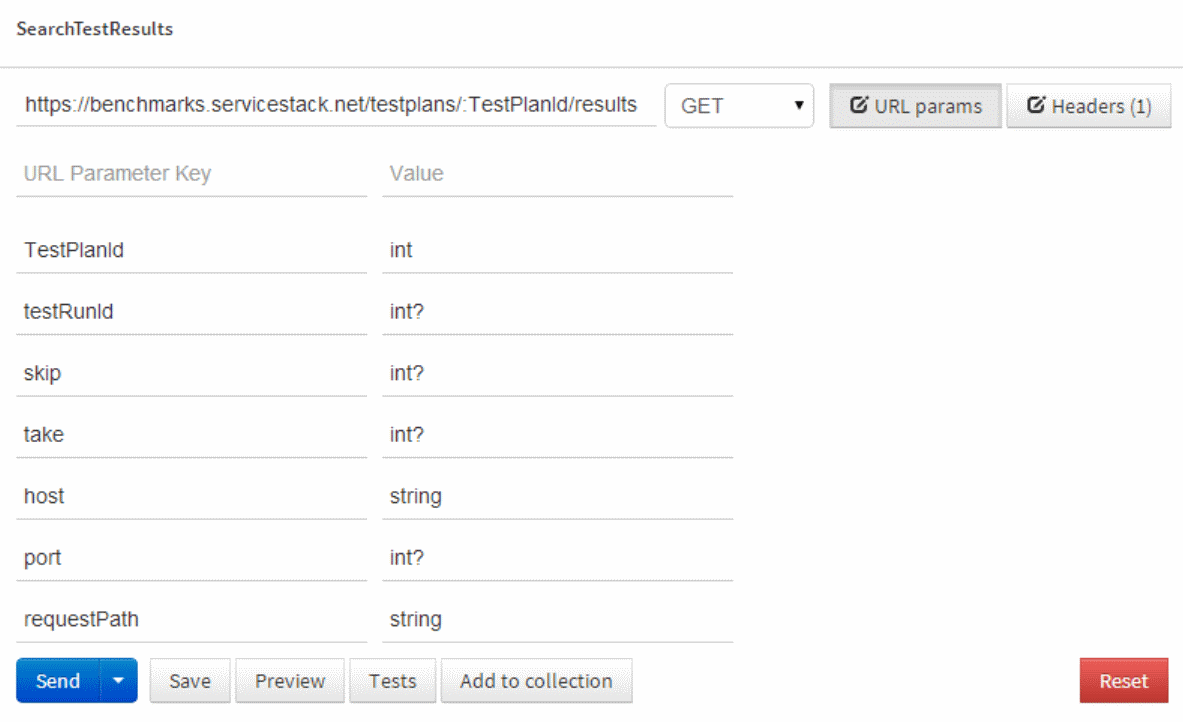
The Path Info variables appear first in the list of available URL params for each service, as seen with TestPlanId above. By default each variable is seeded with its type. Any variables defined on the /pathinfo are sent on the pathinfo whilst other variables in a GET request are sent on the Query String. POST requests also allow sending parameters as form-data.
Support for authenticated requests
Calling authentication-only services can be done with the /postman?exportSession=true parameter which will redirect to a url that captures your session cookies into a deep-linkable url like /postman?ssopt=temp&ssid={key}&sspid={key} that can be copied into Postman.
This lets you replace your session cookies with the session ids on the url, effectively allowing you to take over someone elses session, in this case telling Postman to make requests on your behalf using your authenticated session cookies.
As this functionality is potentially dangerous it's only enabled by default in DebugMode but can be overridden with:
Plugins.Add(new PostmanFeature {
EnableSessionExport = true
});
Other PostmanFeature options
Like other ServiceStack plugins the available options for each Feature can be configured on the Plugin itself at registration:
Registering at a custom path
Use AtRestPath to host the postman metadata route on an alternate:
Plugins.Add(new PostmanFeature {
AtRestPath = "/alt-postman-link" //default /postman
});
Sending Custom HTTP Headers
Use Headers to get Postman to send custom HTTP Headers on each request, e.g:
Plugins.Add(new PostmanFeature {
Headers = "Accept: application/json\nX-Custom-Header: Value",
});
The default is Accept: application/json to ensure each request returns its response as JSON. Multiple headers can be separated with the \n new-line character.
Friendly Type Aliases
The names of the type for Request DTO Property Types displayed can also be customized by adding them to the FriendlyTypeNames Dictionary. E.g. we can show DateTime types as Date in Postmans UI with:
Plugins.Add(new PostmanFeature {
FriendlyTypeNames = { {"DateTime", "Date"} },
});