Utilizing Commands to build more robust and observable systems
Much of ServiceStack has been focused on providing a productive API First Development experience and adding value-added features around your System's external APIs.
Internal API Implementation
Thus far little attention has been given to internal implementations of APIs since it can use anything that fulfils its service contract by returning the APIs populated Response DTO.
How code-bases are structured is largely a matter of developer preference, however we believe we've also been able to add value in this area with the new appealing managed Commands Feature.
Code Architecture
Ultimately nothing beats the simplicity of "No Architecture" by maintaining all logic within a Service Implementation which just needs to call a few App dependencies to implement its functionality and return a populated Response DTO:
public object Any(MyRequest request) => new MyResponse { ... };
This is still the best option for small implementations where the Service is the only consumer of the logic that should be run on the HTTP Worker Request Thread.
When to restructure
Times when you may want to consider moving logic out of your Service into separate classes include:
- Code Reuse: Make it easier to reuse your Service logic in other Services
- Complexity: Break down complex logic into smaller more manageable pieces
- Testability: Make it easier to test your Logic in isolation
- Observability: Make it easier to log and monitor
- Robustness: Make it easier to handle, retry and recover from errors
- Flexibility: Make it easier to run in parallel or in a different managed thread
We'll look at how the new Commands Feature can help in these areas.
Code Reuse
Following principles of YAGNI in doing the simplest thing that could possibly work, whenever we want to reuse logic across Services we'd first start by moving it to an extension method on the dependency that it uses, e.g.
public static async Task<List<Contact>> GetActiveSubscribersAsync(
this IDbConnection db, MailingList mailingList)
{
return await db.SelectAsync(db.From<Contact>(db.TableAlias("c"))
.Where(x => x.DeletedDate == null && x.UnsubscribedDate == null &&
x.VerifiedDate != null && (mailingList & x.MailingLists) == mailingList)
.WhereNotExists(db.From<InvalidEmail>()
.Where<Contact,InvalidEmail>((c,e) =>
e.EmailLower == Sql.TableAlias(c.EmailLower, "c"))
.Select(x => x.Id))
);
}
Which does a great job at encapsulating logic and making it reusable and readable:
foreach (var sub in await Db.GetActiveSubscribersAsync(MailingList.Newsletter)) {
//...
}
Where it can be reused without referencing any external classes whilst also being easily discoverable via intelli-sense.
This works great for 1 or 2 dependencies, but becomes more cumbersome as the number of dependencies grows, e.g:
public static async Task<List<Contact>> GetActiveSubscribersAsync(
this IDbConnection db, ILogger log, ICacheClient cache, MailingList mailingList)
In which the complexity of the extension method dependencies leaks and impacts all calling classes that need to include them and also starts to impact its readability, e.g:
public class MyService(ILogger<MyService> log, ICacheClient cache, IDbConnection db)
: Service
{
public object Any(MyRequest request)
{
var subs = await Db.GetActiveSubscribersAsync(log, cache, request.MailList);
}
}
Refactoring Logic into separate classes
The solution to this is to refactor the logic into a separate class and leverage the IOC to inject the dependencies it needs, fortunately with Primary Constructors this now requires minimal boilerplate code, e.g:
class MyLogic(ILogger<MyService> log, ICacheClient cache, IDbConnection db)
{
//...
}
But it still requires manual registration adding additional complexity to
your Host project Program.cs or Modular Configurations which needs to
manage registration for all these new logic classes, e.g:
builder.Services.AddTransient<MyLogic>();
Commands Feature
Which touches on the first benefit of the Commands Feature which like ServiceStack Services auto registers
all classes implementing the intentionally simple and impl-free IAsyncCommand interface, e.g:
public interface IAsyncCommand<in T>
{
Task ExecuteAsync(T request);
}
Allowing for maximum flexibility in how to implement your logic classes, which are essentially encapsulated units of logic with a single method to execute it, e.g:
public class AddTodoCommand(ILogger<AddTodoCommand> log, IDbConnection db)
: IAsyncCommand<CreateTodo>
{
public async Task ExecuteAsync(CreateTodo request)
{
var newTodo = request.ConvertTo<Todo>();
newTodo.Id = await db.InsertAsync(newTodo, selectIdentity:true);
log.LogDebug("Created Todo {Id}: {Text}", newTodo.Id, newTodo.Text);
}
}
Where we immediately get the benefits of code reuse, encapsulation, and readability without needing to manually register and pollute your App's configuration with them.
By default Commands are registered as transient dependencies, but you can also register them with a different lifetime
scope using the [Lifetime] attribute, e.g:
[Lifetime(Lifetime.Scoped)]
public class AddTodoCommand(ILogger<AddTodoCommand> log, IDbConnection db)
: IAsyncCommand<CreateTodo> {}
Or by manually registering them, if you need a custom registration:
services.AddTransient<AddTodoCommand>(c => CreateAddTodoCommand(c));
Commands with Results
For maximum flexibility, we want to encourage temporal decoupling by separating initiating a command from its execution,
so instead of adding a different method to execute commands with results, we're instead recommending the convention of
storing the result of a command in a Result property, e.g:
public interface IAsyncCommand<in TRequest, out TResult>
: IAsyncCommand<TRequest>, IHasResult<TResult> { }
public interface IHasResult<out T>
{
T Result { get; }
}
So we could implement a command with a result like:
public class AddTodoCommand(ILogger<AddTodoCommand> log, IDbConnection db)
: IAsyncCommand<CreateTodo, Todo>
{
public Todo Result { get; private set; }
public async Task ExecuteAsync(CreateTodo request)
{
Result = request.ConvertTo<Todo>();
Result.Id = await db.InsertAsync(newTodo, selectIdentity:true);
log.LogDebug("Created Todo {Id}: {Text}", Result.Id, Result.Text);
}
}
Ergonomic Base Classes
Often you'll also need to make additional Request Context available to the command that's not apart of the
Command Request or registered from the IOC like an Authenticated User Context or CancellationToken.
To reduce the effort in creating commands with a IRequest context we've added a number ergonomic
base classes to better capture the different call-styles a unit of logic can have including
Sync or Async execution, whether they require Input Arguments or have Result Outputs.
Choosing the appropriate Abstract base class benefits from IDE tooling in generating the method signature that needs to be implemented whilst Async commands with Cancellation Tokens in its method signature highlights any missing async methods that are called without the token.
Sync Commands
SyncCommand- Requires No ArgumentsSyncCommand<TRequest>- Requires TRequest ArgumentSyncCommandWithResult<TResult>- Requires No Args and returns ResultSyncCommandWithResult<TRequest,TResult>- Requires Argument and returns Result
public record MyArgs(int Id);
public record MyResult(string Message);
public class MyCommandNoArgs(ILogger<MyCommandNoArgs> log) : SyncCommand
{
protected override void Run()
{
log.LogInformation("Called with No Args");
}
}
public class MyCommandArgs(ILogger<MyCommandNoArgs> log) : SyncCommand<MyArgs>
{
protected override void Run(MyArgs request)
{
log.LogInformation("Called with {Id}", request.Id);
}
}
public class MyCommandWithResult(ILogger<MyCommandNoArgs> log) : SyncCommandWithResult<MyResult>
{
protected override MyResult Run()
{
log.LogInformation("Called with No Args and returns Result");
return new MyResult("Hello World");
}
}
public class MyCommandWithArgsAndResult(ILogger<MyCommandNoArgs> log)
: SyncCommandWithResult<MyArgs,MyResult>
{
protected override MyResult Run(MyArgs request)
{
log.LogInformation("Called with {Id} and returns Result", request.Id);
return new MyResult("Hello World");
}
}
Async Commands
AsyncCommand- Requires No ArgumentsAsyncCommand<TRequest>- Requires TRequest ArgumentAsyncCommandWithResult<TResult>- Requires No Args and returns ResultAsyncCommandWithResult<TReq,TResult>- Requires Argument and returns Result
public class MyAsyncCommandNoArgs(ILogger<MyCommandNoArgs> log) : AsyncCommand
{
protected override async Task RunAsync(CancellationToken token)
{
log.LogInformation("Async called with No Args");
}
}
public class MyAsyncCommandArgs(ILogger<MyCommandNoArgs> log)
: AsyncCommand<MyArgs>
{
protected override async Task RunAsync(MyArgs request, CancellationToken token)
{
log.LogInformation("Async called with {Id}", request.Id);
}
}
public class MyAsyncCommandWithResult(ILogger<MyCommandNoArgs> log)
: AsyncCommandWithResult<MyResult>
{
protected override async Task<MyResult> RunAsync(CancellationToken token)
{
log.LogInformation("Async called with No Args and returns Result");
return new MyResult("Hello World");
}
}
public class MyAsyncCommandWithArgsAndResult(ILogger<MyCommandNoArgs> log)
: AsyncCommandWithResult<MyArgs,MyResult>
{
protected override async Task<MyResult> RunAsync(
MyArgs request, CancellationToken token)
{
log.LogInformation("Called with {Id} and returns Result", request.Id);
return new MyResult("Hello World");
}
}
Messaging Workflow
For greater resilience and scalability we recommend utilizing a messaging pattern to notify the outputs of a command by publishing messages to invoke dependent logic instead of returning a result, e.g:
Background Jobs
public class AddTodoCommand(IDbConnection db, IBackgroundJobs jobs) : SyncCommand<MyArgs>
{
protected override void Run(MyArgs request)
{
var newTodo = request.ConvertTo<Todo>();
newTodo.Id = db.Insert(newTodo, selectIdentity:true);
// Non Durable Example
jobs.RunCommand<SendNotificationCommand>(
new SendNotification { TodoCreated = newTodo });
// Durable Example
jobs.EnqueueCommand<SendNotificationCommand>(
new SendNotification { TodoCreated = newTodo });
}
}
Background MQ
public class AddTodoCommand(IDbConnection db, IMessageProducer mq) : SyncCommand<MyArgs>
{
protected override void Run(MyArgs request)
{
var newTodo = request.ConvertTo<Todo>();
newTodo.Id = db.Insert(newTodo, selectIdentity:true);
mq.Publish(new SendNotification { TodoCreated = newTodo });
}
}
Which decouples the sender and receiver of the message, allowing it to finish without needing to wait and concern itself on how subsequent logic is processed, e.g. how to handle errors, whether to execute it in a different managed thread, in parallel, etc.
Messaging encourages adopting a more reliable asynchronous one-way workflow instead of implementing logic serially where the sender is timely coupled to the successful execution of all subsequent logic before being able to complete, e.g:
await cmd.ExecuteAsync(createTodo);
var newTodo = cmd.Result;
await SendNewTodoNotificationAsync(newTodo);
It allows for more reliable and observable workflows that removes the temporal coupling between components where each execution step can be executed on different threads, independently monitored and retried if needed.
[A] -> [B] -> [C]
Commands as Application Building Blocks
As they're not dependent on any framework and can support multiple execution patterns, we believe Commands make great building blocks for insulating units of logic as they're simple and testable and allow for managed execution which can easily add logging, monitoring, and resilience around your logic.
Background Jobs or MQ
It should be noted adopting a messaging pattern doesn't require additional infrastructure complexity of an external MQ Server as you can use Background Jobs or Background MQ to execute messages in managed background threads.
Executing Commands
Commands are effectively a pattern to structure your logic that doesn't depend on any implementation assembly or framework, so they can just be executed directly, e.g:
using var db = dbFactory.Open();
var cmd = new AddTodoCommand(new NullLogger<AddTodoCommand>(), db);
await cmd.ExecuteAsync(new CreateTodo { Text = "New Todo" });
Command Executor
They also allow for a managed execution which the CommandsFeature provides with its ICommandExecutor which
can be executed like:
public class MyService(ICommandExecutor executor) : Service
{
public object Any(MyRequest request)
{
var cmd = executor.Command<AddTodoCommand>();
await cmd.ExecuteAsync(new AddTodoCommand { Text = "New Todo" });
}
}
This still results in the same behavior where exceptions are bubbled but also adds observability and resilience and other niceties like executing any Fluent or Declarative Validation on Command Requests.
Retry Failed Commands
We can make commands more resilient by adding the [Retry] attribute to opt into auto retrying failed commands:
[Retry]
public class AddTodoCommand() : IAsyncCommand<CreateTodo> {}
Which will automatically retry the command as per the default Retry Policy:
services.AddPlugin(new CommandsFeature
{
DefaultRetryPolicy = new(
Times: 3,
Behavior: RetryBehavior.FullJitterBackoff,
DelayMs: 100,
MaxDelayMs: 60_000,
DelayFirst: false
)
});
That can be overridden on a per-command basis with the [Retry] attribute, e.g:
[Retry(Times=4, MaxDelayMs=300_000, Behavior=RetryBehavior.LinearBackoff)]
public class AddTodoCommand() : IAsyncCommand<CreateTodo> {}
The different Retry Behaviors available include:
public enum RetryBehavior
{
// Use the default retry behavior
Default,
// Always retry the operation after the same delay
Standard,
// Should be retried with a linear backoff delay strategy
LinearBackoff,
// Should be retried with an exponential backoff strategy
ExponentialBackoff,
// Should be retried with a full jittered exponential backoff strategy
FullJitterBackoff,
}
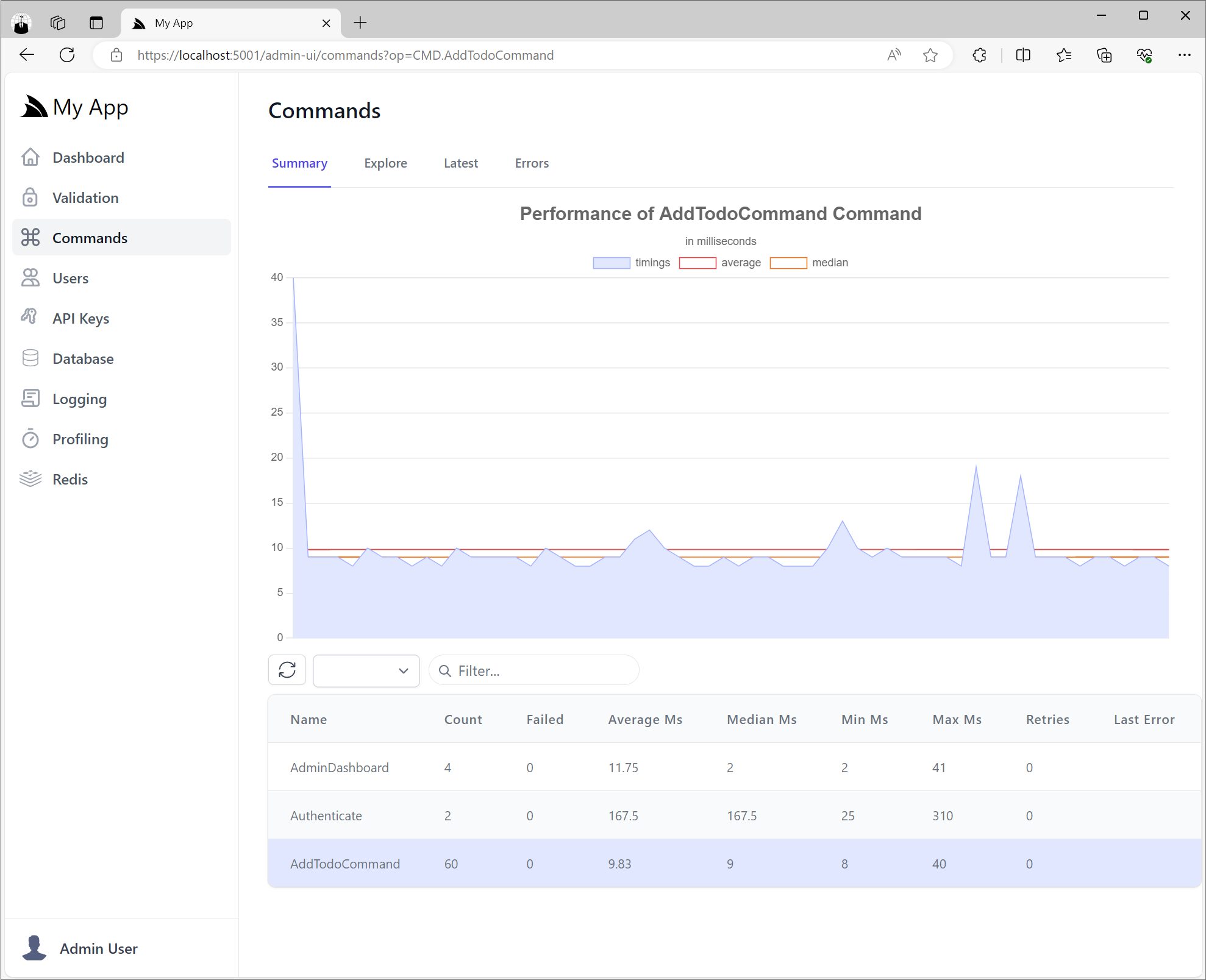
Command Admin UI
Which can be inspected in the new Command Admin UI where you can view summary stats of all executed Commands and APIs in the Summary tab, e.g:
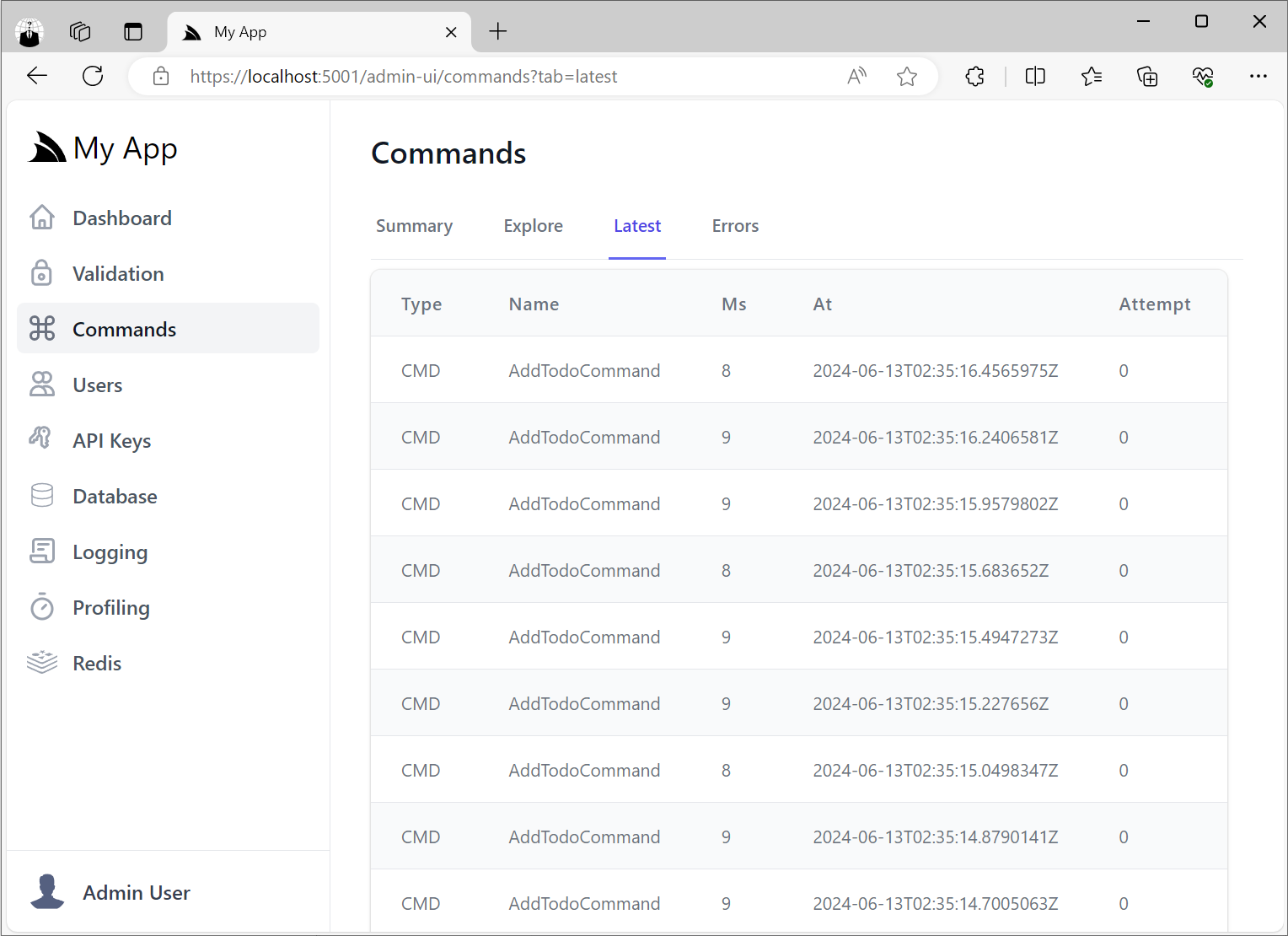
Latest Command Executions
It also maintains a rolling log of the latest executed commands in the Latest tab:
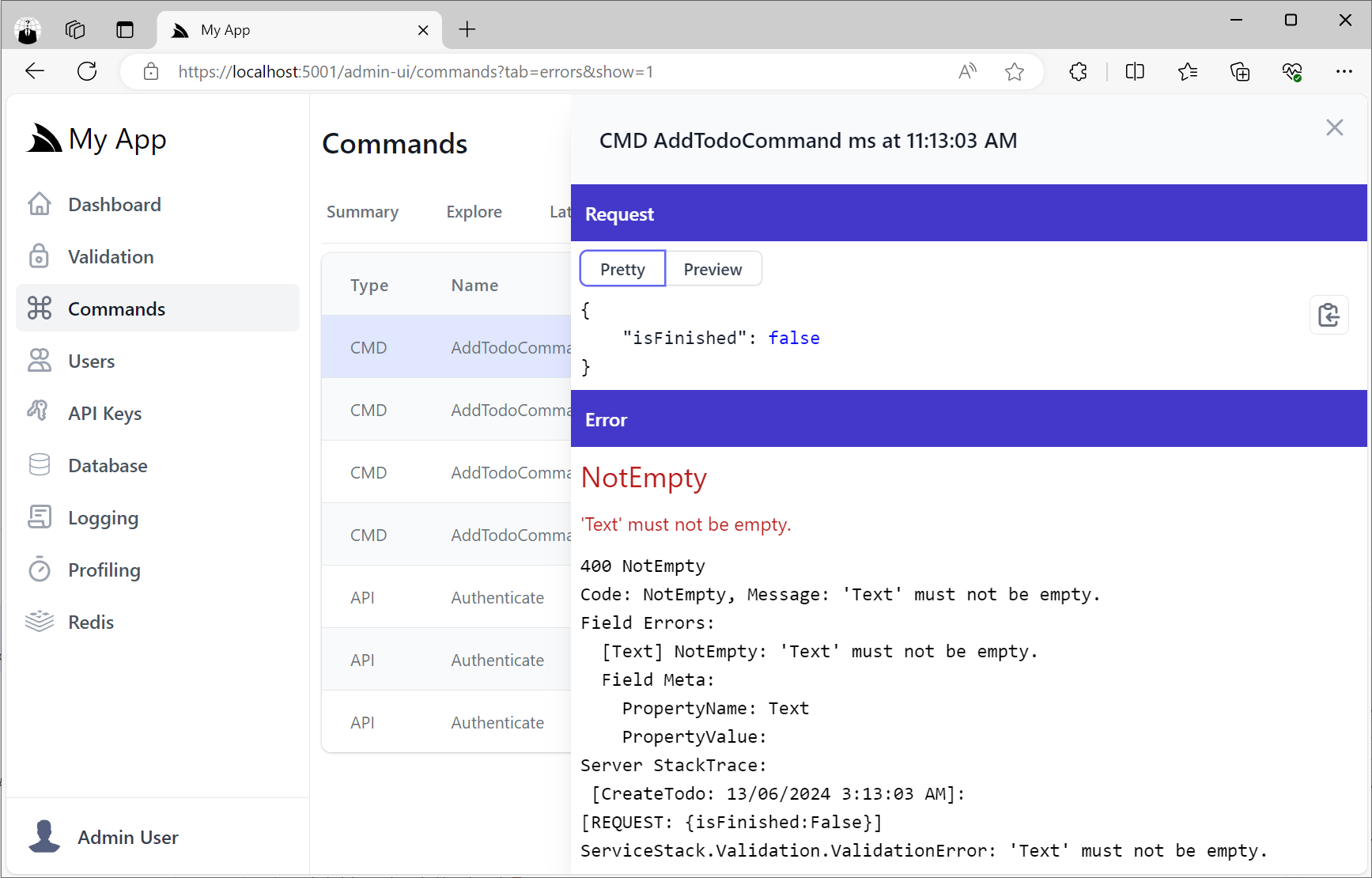
Failed Command Executions
Whilst the Errors tab shows a list of all failed Command and API executions:
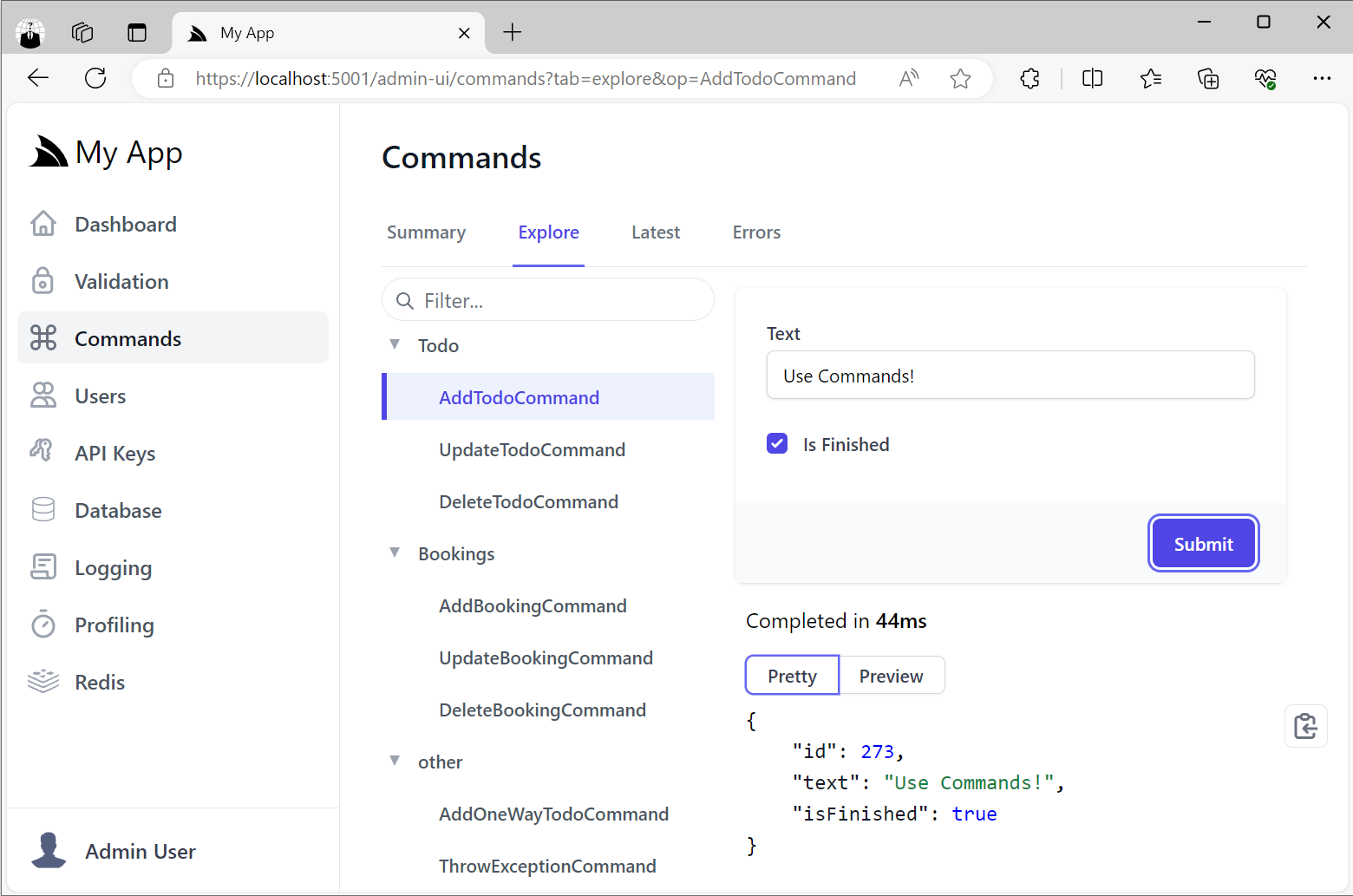
Execute Internal Commands
A benefit of using Commands as the building block for your internal logic is that they enjoy many of the same benefits of ServiceStack's message-based Services where they can be invoked using just the Command Name and a Request Body which allows them to be discovered and executed from the Explore Tab:
In this way they can be treated like Internal APIs for being able to invoke internal functionality that's only accessible by Admin Users.
Group Commands by Tag
Just like ServiceStack Services they can be grouped by Tag which can be used to group related commands:
[Tag("Todos")]
public class AddTodoCommand() : IAsyncCommand<CreateTodo> {}
Execute Commands in Durable Background Jobs
In addition to being able to execute Commands with the ICommandExecutor or from the UI, they can also be executed as part of a Durable Background Job where you'll be able to track and monitor
their progress in real-time.
Background Jobs is already configured in all new Identity Auth Templates in order to send all Identity Auth Emails. Whilst existing Projects can enable it in their .NET 10 Apps with:
npx add-in jobs
Which adds a reference to the ServiceStack.Jobs NuGet package and includes the Modular Startup configuration below:
public class ConfigureBackgroundJobs : IHostingStartup
{
public void Configure(IWebHostBuilder builder) => builder
.ConfigureServices(services => {
services.AddPlugin(new CommandsFeature());
services.AddPlugin(new BackgroundsJobFeature());
services.AddHostedService<JobsHostedService>();
}).ConfigureAppHost(afterAppHostInit: appHost => {
var services = appHost.GetApplicationServices();
var jobs = services.GetRequiredService<IBackgroundJobs>();
// Example of registering a Recurring Job to run Every Hour
//jobs.RecurringCommand<MyCommand>(Schedule.Hourly);
});
}
public class JobsHostedService(ILogger<JobsHostedService> log, IBackgroundJobs jobs)
: BackgroundService
{
protected override async Task ExecuteAsync(CancellationToken stoppingToken)
{
await jobs.StartAsync(stoppingToken);
using var timer = new PeriodicTimer(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3));
while (!stoppingToken.IsCancellationRequested &&
await timer.WaitForNextTickAsync(stoppingToken))
{
await jobs.TickAsync();
}
}
}
Background MQ Integration
Although CommandsFeature is a standalone feature it can also be configured and used along with Background MQ which is a good option if you intend on adopting another Message Queue Broker in
your App's in future.
public class ConfigureMq : IHostingStartup
{
public void Configure(IWebHostBuilder builder) => builder
.ConfigureServices((context, services) => {
services.AddSingleton<IMessageService>(c => new BackgroundMqService());
services.AddPlugin(new CommandsFeature());
})
.ConfigureAppHost(afterAppHostInit: appHost => {
var mqService = appHost.Resolve<IMessageService>();
//Register ServiceStack APIs you want to be able to invoke via MQ
mqService.RegisterHandler<SendEmail>(appHost.ExecuteMessage);
mqService.Start();
});
}
Despite being 2 independent features, they work well together as the Background MQ can be used to execute Commands in managed background threads of which a single thread is used to execute each Request Type by default (configurable per request).
You'd typically want to use queues to improve scalability by reducing locking and concurrency contention of heavy resources by having requests queued and executed in a managed background thread where it's able to execute requests as fast as it can without contention. Queues are also a great solution for working around single thread limitations of resources like writes to SQLite databases.
Use Case - SQLite Writes
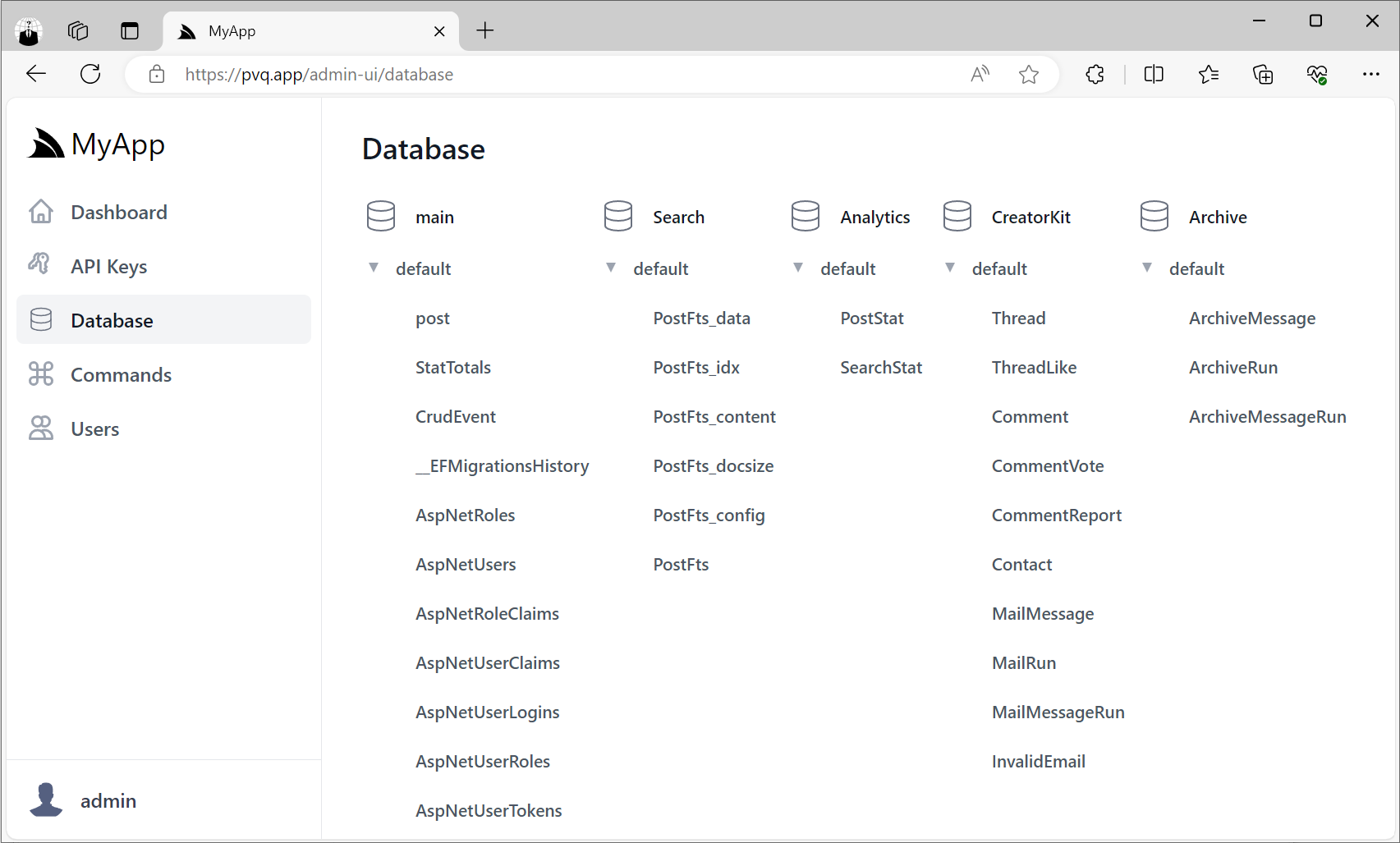
As we've started to use server-side SQLite databases for our new Apps given its many benefits we needed a solution to workaround its limitation of not being able to handle multiple writes concurrently.
One of the benefits of using SQLite is creating and managing multiple databases is relatively cheap, so we can mitigate this limitation somewhat by maintaining different subsystems in separate databases, e.g:
But each database can only be written to by a single thread at a time, which we can now easily facilitate with Background Jobs or MQ Command DTOs.
In all cases we recommend using Sync DB APIs for SQLite since their underlying implementation always blocks.
Queuing DB Writes with SyncCommand Background Jobs
One way to remove contention is to serially execute DB Writes which we can do by executing DB Writes within SyncCommand* and using a named [Worker(Workers.AppDb)] attribute for Writes to the primary database, e.g:
[Worker(Workers.AppDb)]
public class DeleteCreativeCommand(IDbConnection db)
: SyncCommand<DeleteCreative>
{
protected override void Run(DeleteCreative request)
{
var artifactIds = request.ArtifactIds;
db.Delete<AlbumArtifact>(x => artifactIds.Contains(x.ArtifactId));
db.Delete<ArtifactReport>(x => artifactIds.Contains(x.ArtifactId));
db.Delete<ArtifactLike>(x => artifactIds.Contains(x.ArtifactId));
db.Delete<Artifact>(x => x.CreativeId == request.Id);
db.Delete<CreativeArtist>(x => x.CreativeId == request.Id);
db.Delete<CreativeModifier>(x => x.CreativeId == request.Id);
db.Delete<Creative>(x => x.Id == request.Id);
}
}
Other databases should use its named connection for its named worker, e.g:
[Worker(Databases.Search)]
public class DeleteSearchCommand(IDbConnectionFactory dbFactory)
: SyncCommand<DeleteSearch>
{
protected override void Run(DeleteSearch request)
{
using var db = dbFactory.Open(Databases.Search);
db.DeleteById<ArtifactFts>(request.Id);
//...
}
}
Example of a DB Write command with result:
[Worker(Databases.Albums)]
public class CreateAlbumCommand(IDbConnectionFactory dbFactory)
: SyncCommandWithResult<CreateAlbum,Album>
{
protected override Album Run(CreateAlbum request)
{
using var db = dbFactory.Open(Databases.Albums);
var album = request.ConvertTo<Album>();
album.Id = db.Insert(album, selectIdentity:true);
foreach (var artifact in request.Artifacts)
{
artifact.AlbumId = album.Id;
db.Insert(artifact);
}
return album;
}
}
Where it will be executed within its Database Lock.
Running Commands
You'll typically want to run DB Write Commands with RunCommand* APIs which are a faster and lighter weight
alternative then durable jobs which are persisted in the jobs.db before execution.
Everytime commands are executed they'll be added to a ConcurrentQueue of the specified worker. Commands delegated to different named workers execute concurrently, whilst commands with the same worker are executed serially.
When using any SyncCommand* base class, its execution still uses database locks
but any contention is alleviated as they're executed serially by a single worker thread.
public class MyServices(IBackgroundJobs jobs) : Service
{
// Returns immediately with a reference to the Background Job
public object Any(DeleteCreative request)
{
// Queues a durable job to execute the command with the AppDb Worker
var jobRef = jobs.EnqueueCommand<DeleteCreativeCommand>(request);
// Executes Command with Databases.Search worker
jobs.EnqueueCommand<DeleteSearchCommand>(new DeleteSearch {
Id = request.ArtifactId
});
return jobRef;
}
// Returns after the command is executed with its result (if any)
public async Task Any(CreateAlbum request)
{
// Executes a transient (i.e. non-durable) job with the named worker
var album = await jobs.RunCommandAsync<CreateAlbumCommand>(request);
return album;
}
}
MQ Command DTOs
If using Background MQ we can use the [Command] attribute to be able to execute multiple commands on a single Request DTO Properties:
[Tag(Tag.Tasks)]
[Restrict(RequestAttributes.MessageQueue), ExcludeMetadata]
public class DbWrites : IGet, IReturn<EmptyResponse>
{
[Command<CreatePostVoteCommand>]
public Vote? CreatePostVote { get; set; }
[Command<CreateCommentVoteCommand>]
public Vote? CreateCommentVote { get; set; }
[Command<CreatePostCommand>]
public Post? CreatePost { get; set; }
[Command<UpdatePostCommand>]
public Post? UpdatePost { get; set; }
[Command<DeletePostsCommand>]
public DeletePosts? DeletePosts { get; set; }
[Command<DeleteAnswersCommand>]
public DeleteAnswers? DeleteAnswers { get; set; }
[Command<CreateAnswerCommand>]
public Post? CreateAnswer { get; set; }
[Command<PostSubscriptionsCommand>]
public PostSubscriptions? PostSubscriptions { get; set; }
[Command<TagSubscriptionsCommand>]
public TagSubscriptions? TagSubscriptions { get; set; }
//...
}
Then to execute the commands we can use the Request.ExecuteCommandsAsync extension method for its
Background MQ API implementation:
public class BackgroundMqServices : Service
{
public Task Any(DbWrites request) => Request.ExecuteCommandsAsync(request);
}
Which goes through all Request DTO properties to execute all populated properties with their associated command, using it as the request for the command.
So after registering the DbWrites Command DTO with the MQ Service:
mqService.RegisterHandler<DbWrites>(appHost.ExecuteMessage);
We can now publish a single DbWrites message to execute multiple commands in a single managed background thread:
public class NotificationServices(MessageProducer mq) : Service
{
public object Any(Watch request)
{
var userName = Request.GetClaimsPrincipal().GetUserName();
mq.Publish(new DbWrites
{
PostSubscriptions = request.PostId == null ? null : new()
{
UserName = userName,
Subscriptions = [request.PostId.Value],
},
TagSubscriptions = request.Tag == null ? null : new()
{
UserName = userName,
Subscriptions = [request.Tag],
},
});
mq.Publish(new AnalyticsTasks {
WatchRequest = request,
});
}
}
We also benefit from its natural parallelism where write requests to different Databases are executed in parallel.