The @servicestack/client library enables the best end-to-end typed developer experience for calling ServiceStack APIs in any TypeScript or JavaScript project.
Usage in TypeScript or npm projects
Projects using TypeScript or any npm build system can install the dependency-free library with:
npm install @servicestack/client
Which can be used with your APIs typed DTOs that TypeScript projects can generate using TypeScript Add ServiceStack Reference with:
x ts https://localhost:5001
Which will save your API DTOs to dtos.ts that can be referenced in your code with:
import { Hello } from "./dtos"
JavaScript npm projects
Non-TypeScript npm projects can choose to either have TypeScript generate the DTOs into the preferred JavaScript target:
tsc dtos.ts
Alternatively they can generate ES6 annotated DTOs using JavaScript Add ServiceStack Reference with:
x mjs https://localhost:5001
Which will save your API DTOs to dtos.mjs where they can be referenced in your code with:
import { Hello } from "./dtos.mjs"
Example Usage
Either solution gives you the same productive end-to-end Typed API access, e.g:
import { JsonServiceClient } from "@servicestack/client"
const client = new JsonServiceClient()
const api = await client.api(new Hello({ Name: 'World' }))
if (api.succeeded) {
console.log(api.response.result)
} else {
console.log(api.error)
}
Usage in .NET Apps without npm
Modern JavaScript Apps not using an npm build system like the Razor Vue Tailwind templates can download @servicestack/client from:
- https://unpkg.com/@servicestack/client@2/dist/servicestack-client.mjs
- https://unpkg.com/@servicestack/client@2/dist/servicestack-client.min.mjs (minified)
Then use an importmap to specify where to load @servicestack/client from, e.g:
<script async src="https://ga.jspm.io/npm:es-module-shims@1.6.3/dist/es-module-shims.js"></script><!--safari-->
<script type="importmap">
{
"imports": {
"@servicestack/client": "/js/servicestack-client.mjs"
}
}
</script>
ImportMap in Razor Pages or MVC
Razor Pages or MVC projects can use @Html.ImportMap() in _Layout.cshtml to use different builds for development and production, e.g:
@if (Context.Request.Headers.UserAgent.Any(x => x.Contains("Safari") && !x.Contains("Chrome")))
{
<script async src="https://ga.jspm.io/npm:es-module-shims@1.6.3/dist/es-module-shims.js"></script>
}
@Html.ImportMap(new()
{
["@servicestack/client"] = ("/js/servicestack-client.mjs", "/js/servicestack-client.min.mjs"),
})
This lets your source code reference the library by package name to enable using the same source code in a JavaScript Module, e.g:
<script type="module">
import { JsonServiceClient } from "@servicestack/client"
const client = new JsonServiceClient()
const api = await client.api(new Hello({ Name: 'World' }))
</script>
JavaScript API DTOs
Your JavaScript API DTOs can either directly reference the /types/mjs endpoint:
import { Hello } from '/types/mjs'
Enable static analysis and intelli-sense
Or for better IDE intelli-sense during development, save the annotated Typed DTOs to disk with the x dotnet tool:
x mjs
Then reference it instead to enable IDE static analysis when calling Typed APIs from JavaScript:
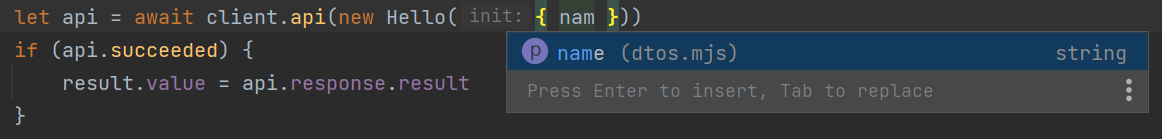
import { Hello } from '/js/dtos.mjs'
client.api(new Hello({ name }))
To also enable static analysis for @servicestack/client, install the dependency-free library as a dev dependency:
npm install -D @servicestack/client
Where only its TypeScript definitions are used by the IDE during development to enable its type-checking and intelli-sense.
Support Legacy Browsers
JavaScript Projects needing to support legacy browsers can use ES3 Common.js DTOs to
enable access using old-style <script> includes.
JsonServiceClient
To create JsonServiceClient instances in v6+ projects using the JSON /api route use:
const client = new JsonServiceClient(baseUrl)
Where it's configured to not use any JSON HTTP Headers to enable more efficient CORS requests without preflight requests.
Alternatively if needed you can use useBasePath() to revert back to using legacy /json/reply pre-defined Routes:
const client = new JsonServiceClient(baseUrl).useBasePath()
API Reference
API method
The api returns a typed ApiResult<Response> Value Result that encapsulates either a Typed Response or a
structured API Error populated in ResponseStatus allowing you to handle API responses programmatically without
try/catch handling:
const api = client.api(new Hello({ name }))
if (api.failed) {
console.log(`Greeting failed! ${e.errorCode}: ${e.errorMessage}`);
return;
}
console.log(`API Says: ${api.response.result}`) //api.succeeded
Simplified API Handling
Being able to treat errors as values greatly increases the ability to programmatically handle and genericise api handling and greatly simplifies functionality needing to handle both successful and error responses like binding to UI components.
An example of this is below where we're able to concurrently fire off multiple unrelated async requests in parallel, wait for them all to complete, print out the ones that have succeeded or failed then access their strong typed responses:
import { JsonServiceClient } from "@servicestack/client"
let requests:ApiRequest[] = [
new AppOverview(), // GET => AppOverviewResponse
new DeleteTechnology(), // DELETE => IReturnVoid (requires auth)
new GetAllTechnologies(), // GET => GetAllTechnologiesResponse
new GetAllTechnologyStacks(), // GET => GetAllTechnologyStacksResponse
]
let results = await Promise.all(requests.map(async (request) =>
({ request, api:await client.api(request) as ApiResponse}) ))
let failed = results.filter(x => x.api.failed)
console.log(`${failed.length} failed:`)
failed.forEach(x =>
console.log(` ${x.request.getTypeName()} Request Failed: ${failed.map(x => x.api.errorMessage)}`))
let succeeded = results.filter(x => x.api.succeeded)
console.log(`\n${succeeded.length} succeeded: ${succeeded.map(x => x.request.getTypeName()).join(', ')}`)
let r = succeeded.find(x => x.request.getTypeName() == 'AppOverview')?.api.response as AppOverviewResponse
if (r) console.log(`Top 5 Technologies: ${r.topTechnologies.slice(0,4).map(tech => tech.name).join(', ')}`)
Output:
1 failed
DeleteTechnology Request Failed: Unauthorized
3 succeeded: AppOverview, GetAllTechnologies, GetAllTechnologyStacks
Top 5 Technologies: Redis, MySQL, Amazon EC2, Nginx
Being able to treat Errors as values has dramatically reduced the effort required to accomplish the same feat if needing
to handle errors with try/catch.
Ideal Typed Message-based API
The TypeScript JsonServiceClient enables the same productive, typed API development experience available
in ServiceStack's other 1st-class supported client platforms.
The JsonServiceClient leverages the additional type hints ServiceStack embeds in each TypeScript Request DTO
to achieve the ideal typed, message-based API - so all API requests benefit from a succinct, boilerplate-free
Typed API.
Here's a quick look at what it looks like. The example below shows how to create a
C# Gist in Gistlyn
after adding a TypeScript ServiceStack Reference
to gistlyn.com and installing the @servicestack/client
npm package:
import { JsonServiceClient } from '@servicestack/client';
import { StoreGist, GithubFile } from './dtos';
const client = new JsonServiceClient("https://gistlyn.com");
const request = new StoreGist({
files: {
[file.filename]: new GithubFile({
filename: 'main.cs',
content: 'var greeting = "Hi, from TypeScript!";'
})
}
})
const api = client.api(request); //response:StoreGistResponse
if (api.succeeded) {
console.log(`New C# Gist was created with id: ${r.gist}`);
location.href = `https://gist.cafe/${r.gist}`;
} else {
console.log("Failed to create Gist: ", e.errorMessage);
}
Where the response param is typed to StoreGistResponse DTO Type.
Sending additional arguments with Typed API Requests
Many AutoQuery Services utilize implicit conventions to query fields that aren't explicitly defined on AutoQuery Request DTOs, these can now be queried by specifying additional arguments with the typed Request DTO, e.g:
//typed to QueryResponse<TechnologyStack>
const response = await client.get(new FindTechStacks(), { VendorName: "ServiceStack" });
Which will return TechStacks developed by ServiceStack.
Calling APIs with Custom URLs
You can call Services using relative or absolute urls, e.g:
client.get<GetTechnologyResponse>("/technology/ServiceStack")
client.get<GetTechnologyResponse>("http://techstacks.io/technology/ServiceStack")
// GET http://techstacks.io/technology?Slug=ServiceStack
client.get<GetTechnologyResponse>("/technology", { Slug: "ServiceStack" })
as well as POST Request DTOs to custom urls:
client.postToUrl("/custom-path", request, { Slug: "ServiceStack" });
client.putToUrl("http://example.org/custom-path", request);
Raw Data Responses
The JsonServiceClient also supports Raw Data responses like string and byte[] which also get a Typed API
once declared on Request DTOs using the IReturn<T> marker:
public class ReturnString : IReturn<string> {}
public class ReturnBytes : IReturn<byte[]> {}
Which can then be accessed as normal, with their Response typed to a JavaScript string or Uint8Array for
raw byte[] responses:
let str:string = await client.get(new ReturnString());
let data:Uint8Array = await client.get(new ReturnBytes());
Authenticating using Basic Auth
Basic Auth support is implemented in JsonServiceClient and follows the same API made available in the C#
Service Clients where the userName/password properties can be set individually, e.g:
var client = new JsonServiceClient(baseUrl);
client.userName = user;
client.password = pass;
const response = await client.get(new SecureRequest());
Or use client.setCredentials() to have them set both together.
Authenticating using Credentials
Alternatively you can authenticate using userName/password credentials by
adding a TypeScript Reference
to your remote ServiceStack Instance and sending a populated Authenticate Request DTO, e.g:
const response = await client.post(new Authenticate({
provider: "credentials", userName, password, rememberMe: true }));
This will populate the JsonServiceClient with
Session Cookies
which will transparently be sent on subsequent requests to make authenticated requests.
Authenticating using JWT
Use the bearerToken property to Authenticate with a ServiceStack JWT Provider using a JWT Token:
client.bearerToken = jwtToken;
Alternatively you can use a Refresh Token instead:
client.refreshToken = refreshToken;
Authenticating using an API Key
Use the bearerToken property to Authenticate with an API Key:
client.bearerToken = apiKey;
Transparently handle 401 Unauthorized Responses
If the server returns a 401 Unauthorized Response either because the client was Unauthenticated or the
configured Bearer Token or API Key used had expired or was invalidated, you can use onAuthenticationRequired
callback to re-configure the client before automatically retrying the original request, e.g:
client.onAuthenticationRequired = async () => {
const authClient = new JsonServiceClient(authBaseUrl);
authClient.userName = userName;
authClient.password = password;
const response = await authClient.get(new Authenticate());
client.bearerToken = response.bearerToken;
};
//Automatically retries requests returning 401 Responses with new bearerToken
var response = await client.get(new Secured());
Automatically refresh Access Tokens
With the Refresh Token support in JWT
you can use the refreshToken property to instruct the Service Client to automatically fetch new
JWT Tokens behind the scenes before automatically retrying failed requests due to invalid or expired JWTs, e.g:
//Authenticate to get new Refresh Token
const authClient = new JsonServiceClient(authBaseUrl);
authClient.userName = userName;
authClient.password = password;
const authResponse = await authClient.get(new Authenticate());
//Configure client with RefreshToken
client.refreshToken = authResponse.RefreshToken;
//Call authenticated Services and clients will automatically retrieve new JWT Tokens as needed
const response = await client.get(new Secured());
Use the refreshTokenUri property when refresh tokens need to be sent to a different ServiceStack Server, e.g:
client.refreshToken = refreshToken;
client.refreshTokenUri = authBaseUrl + "/access-token";
ServerEvents Client
The TypeScript ServerEventClient is an idiomatic port of ServiceStack's C# Server Events Client in native TypeScript providing a productive client to consume ServiceStack's real-time Server Events that can be used in TypeScript Web, Node.js Server and React Native iOS and Android Mobile Apps.
const channels = ["home"];
const client = new ServerEventsClient("/", channels, {
handlers: {
onConnect: (sub:ServerEventConnect) => { // Successful SSE connection
console.log("You've connected! welcome " + sub.displayName);
},
onJoin: (msg:ServerEventJoin) => { // User has joined subscribed channel
console.log("Welcome, " + msg.displayName);
},
onLeave: (msg:ServerEventLeave) => { // User has left subscribed channel
console.log(msg.displayName + " has left the building");
},
onUpdate: (msg:ServerEventUpdate) => { // User channel subscription was changed
console.log(msg.displayName + " channels subscription were updated");
},
onMessage: (msg:ServerEventMessage) => {},// Invoked for each other message
//... Register custom handlers
announce: (text:string) => {}, // Handle messages with simple argument
chat: (chatMsg:ChatMessage) => {}, // Handle messages with complex type argument
CustomMessage: (msg:CustomMessage) => {}, // Handle complex types with default selector
},
receivers: {
//... Register any receivers
tv: {
watch: function (id) { // Handle 'tv.watch {url}' messages
var el = document.querySelector("#tv");
if (id.indexOf('youtu.be') >= 0) {
var v = splitOnLast(id, '/')[1];
el.innerHTML = templates.youtube.replace("{id}", v);
} else {
el.innerHTML = templates.generic.replace("{id}", id);
}
el.style.display = 'block';
},
off: function () { // Handle 'tv.off' messages
var el = document.querySelector("#tv");
el.style.display = 'none';
el.innerHTML = '';
}
}
},
onException: (e:Error) => {}, // Invoked on each Error
onReconnect: (e:Error) => {} // Invoked after each auto-reconnect
})
.addListener("theEvent",(e:ServerEventMessage) => {}) // Add listener for pub/sub event trigger
.start(); // Start listening for Server Events!
When publishing a DTO Type for your Server Events message, your clients will be able to benefit from the generated DTOs in TypeScript ServiceStack References.
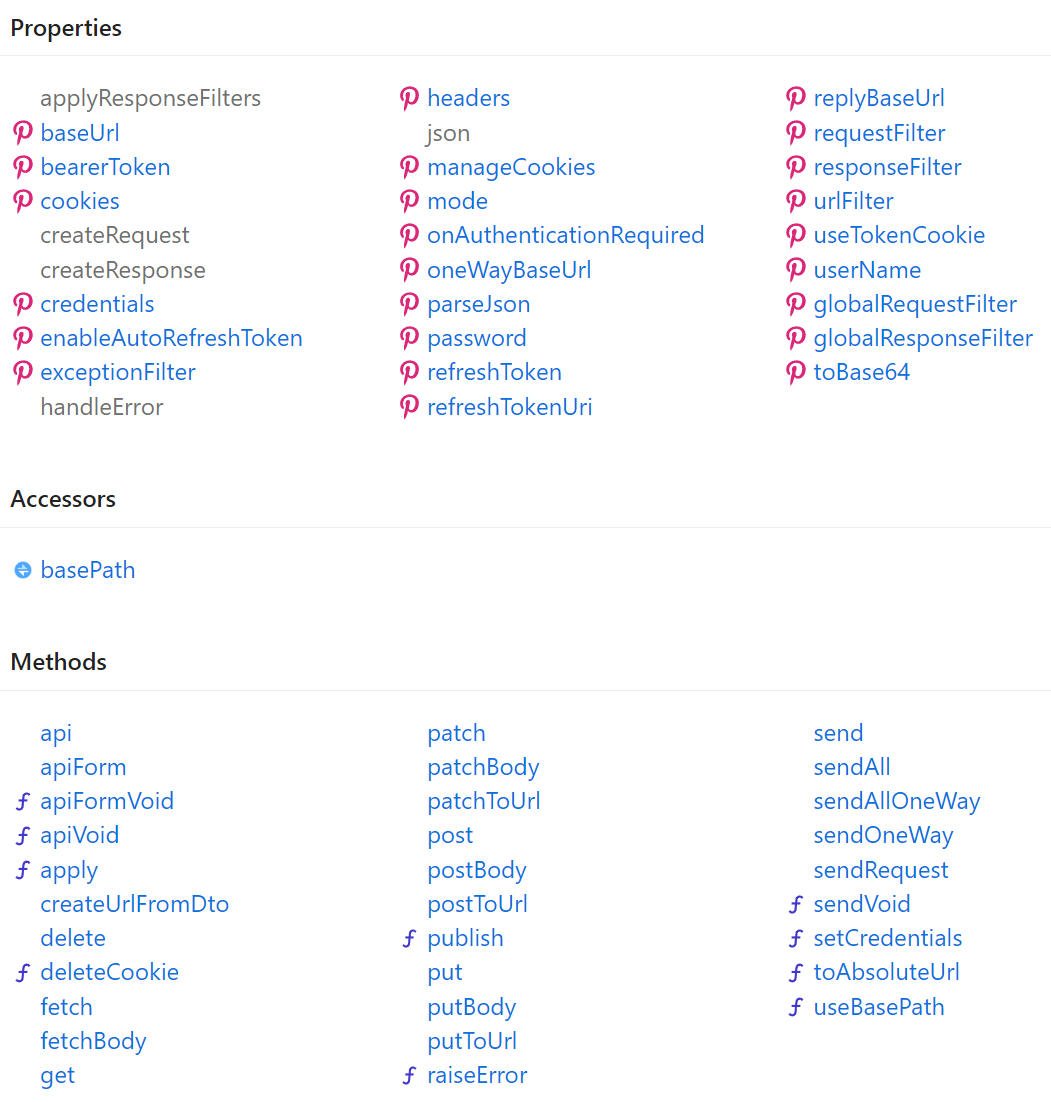
Rich intelli-sense support
Even pure HTML/JS Apps that don't use TypeScript or any external dependencies will still benefit from the Server
generated dtos.ts and TypeScript definitions where you'll be able to benefit from rich intelli-sense support
in smart IDEs like Rider for both the client library:
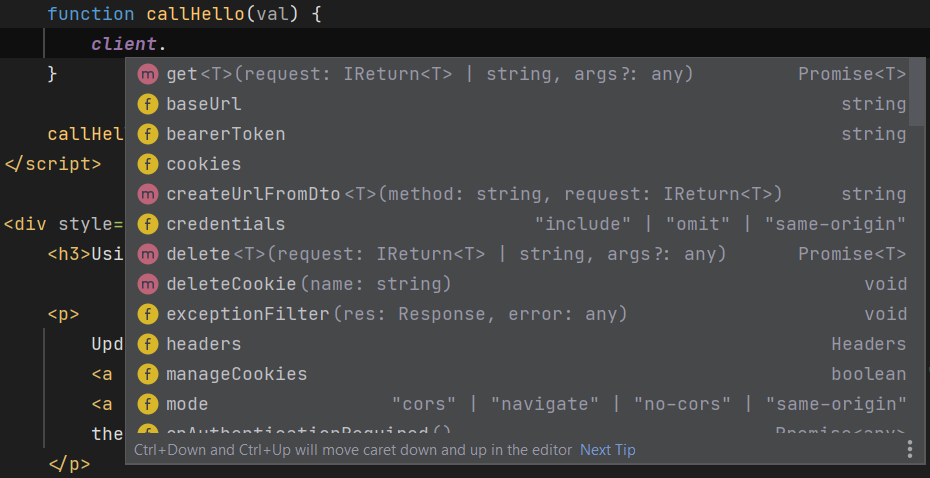
As well as your App's server generated DTOs: