ServiceStack pre-release GitHub Feed
Our interim pre-release NuGet packages in between major releases on NuGet are published to GitHub.
TIP
If preferred, the pre-release packages are also available in our feedz.io or MyGet package feeds.
Requires GitHub Authentication
Since GitHub does not yet support anonymous access to public NuGet repositories, you will need to configure a GitHub Personal Access Token with read:packages permissions.
Once your GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT) is created, you will need to add a servicestack-github NuGet Source into your NuGet.config.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<packageSources>
<add key="nuget.org" value="https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json" protocolVersion="3" />
<add key="github-servicestack" value="https://nuget.pkg.github.com/ServiceStack/index.json" />
</packageSources>
<packageSourceCredentials>
<github-servicestack>
<add key="Username" value="GITHUB_USERNAME" />
<add key="ClearTextPassword" value="TOKEN" />
</github-servicestack>
</packageSourceCredentials>
</configuration>
Your packageSources key needs to match the packageSourceCredentials element name
Add using Mix
If you have the dotnet x tool installed, you can configure your projects by downloading NuGet.Config in the same folder as your .sln
npx add-in gh-nuget
Using GitHub Packages in GitHub Actions
To avoid checking in Tokens into your repositories, the GitHub Packages Registry should instead be added as a nuget source from the command-line where it has access to your Repo's secrets. This will need to be added before building or publishing your .NET project, e.g:
build.yml
- name: Add pre-release packages source
run: |
dotnet nuget add source "https://nuget.pkg.github.com/ServiceStack/index.json" --username ${{ github.actor }} --password ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} --store-password-in-clear-text --name github
- name: Build
run: dotnet build
release.yml
# Publish .NET Project
- name: Publish dotnet project
working-directory: ./MyApp
run: |
dotnet nuget add source "https://nuget.pkg.github.com/ServiceStack/index.json" --username ${{ github.actor }} --password ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} --store-password-in-clear-text --name github
dotnet publish -c Release
Adding nuget source in Dockerfile
If restoring and building your project from inside your Dockerfile you can use Docker secrets to pass these credentials from your GitHub Action to your Dockerfile:
release.yml
- name: Build and push API Docker image
uses: docker/build-push-action@v4
if: ${{ github.event.inputs.version == '' || github.event.inputs.version == 'latest' }}
with:
file: Dockerfile
context: .
push: true
tags: ghcr.io/${{ env.image_repository_name }}:${{ env.TAG_NAME }}
secrets: |
github_actor=${{ github.actor }}
github_token=${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
Dockerfile
These can be accessed to add a nuget source in the same RUN command as dotnet restore with:
RUN --mount=type=secret,id=github_actor \
--mount=type=secret,id=github_token \
export github_actor=$(cat /run/secrets/github_actor) && \
export github_token=$(cat /run/secrets/github_token) && \
dotnet nuget add source "https://nuget.pkg.github.com/ServiceStack/index.json" --username $github_actor --password $github_token --store-password-in-clear-text --name github && \
dotnet restore
Add using VS .NET
Instructions to add ServiceStack's GitHub feed to VS .NET are:
- Go to Tools > Options > Nuget Package Manager > Package Sources
- Add the Source
https://nuget.pkg.github.com/ServiceStack/index.jsonwith the name of your choice, e.g. servicestack-github - Enter your GitHub Username and Personal Access Token when prompted.
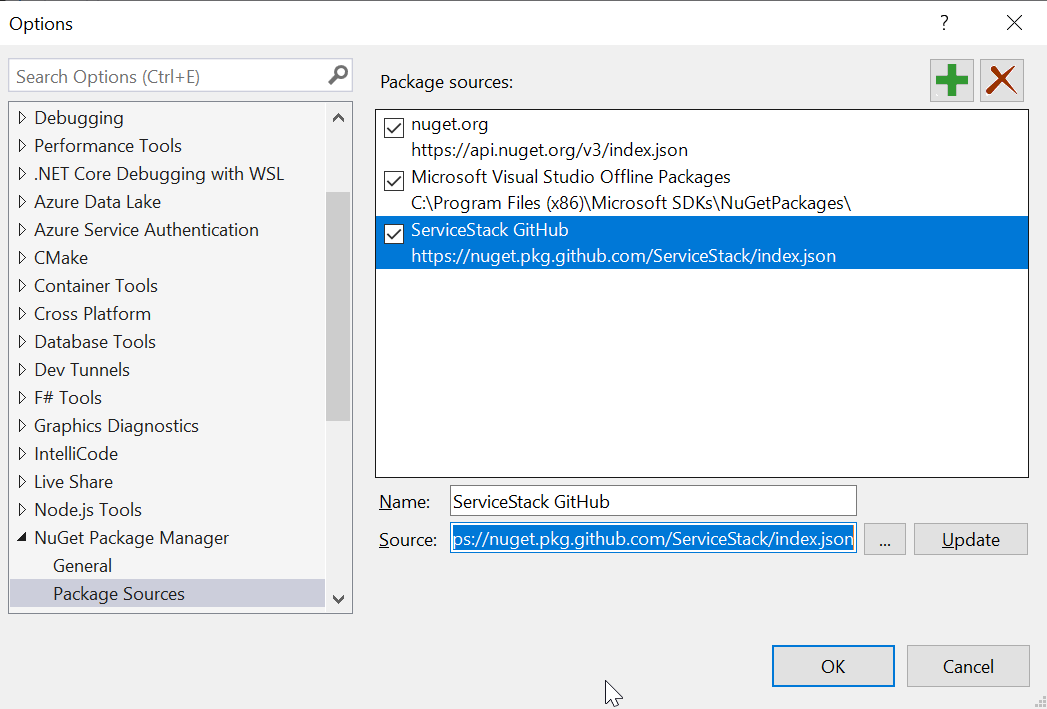
After registering the GitHub feed it will show up under NuGet package sources when opening the NuGet package manager dialog:
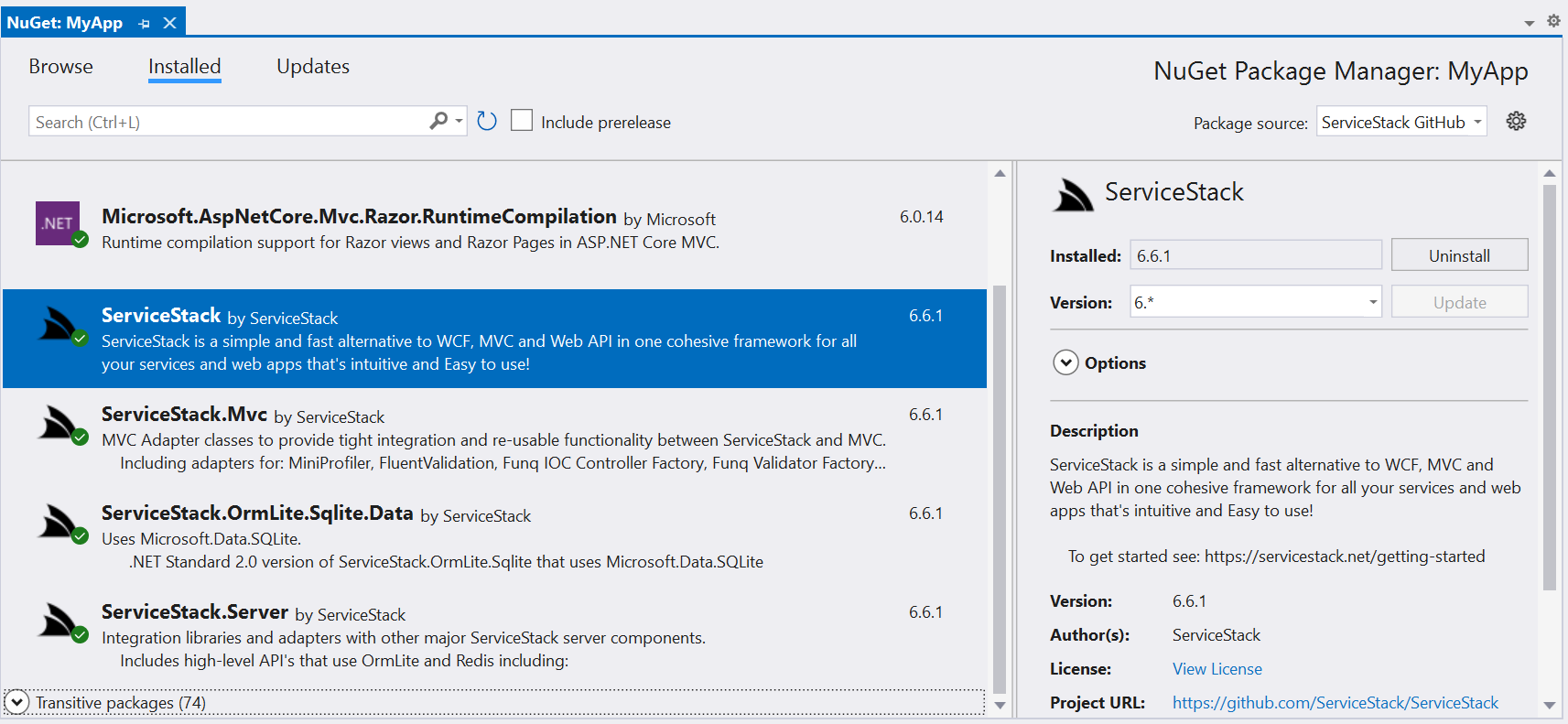
Which will allow you to search and install pre-release packages from the selected GitHub feed.
INFO
You can configure your Package Source Credentials outside of Visual Studio via a NuGet.config.
Your NuGet.config should be located under %AppData%\NuGet\NuGet.config or ~/.nuget/NuGet/NuGet.config
Adding GitHub feed without VS .NET
If you're not using or don't have VS .NET installed, you can add the GitHub feed to your NuGet.config at %AppData%\NuGet\NuGet.config or ~/.nuget/NuGet/NuGet.config:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<packageSources>
<add key="nuget.org" value="https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json" protocolVersion="3" />
<add key="github-servicestack" value="https://nuget.pkg.github.com/ServiceStack/index.json" />
</packageSources>
<packageSourceCredentials>
<github-servicestack>
<add key="Username" value="GITHUB_USERNAME" />
<add key="ClearTextPassword" value="TOKEN" />
</github-servicestack>
</packageSourceCredentials>
</configuration>
Redownloading GitHub packages
If you've already packages with the same version number from GitHub previously installed, you will
need to manually delete the NuGet /packages folder for NuGet to pull down the latest packages.
Clear NuGet Package Cache
You can clear your local NuGet packages cache in any OS by running the command-line below in your favorite Terminal:
nuget locals all -clear
If nuget is not in your Systems PATH, it can also be invoked from the dotnet tool:
dotnet nuget locals all --clear
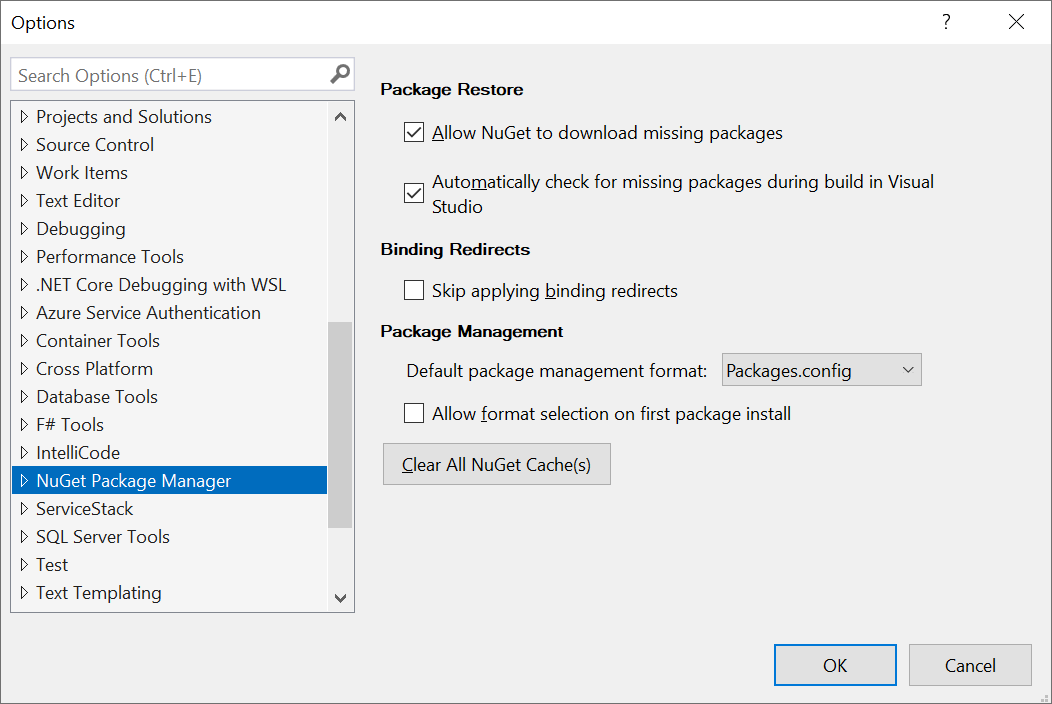
Within VS .NET you can clear them from Tools > Options > Nuget Package Manager and click Clear All NuGet Cache(s):
Alternatively on Windows you can delete the Cached NuGet packages manually with:
del %LOCALAPPDATA%\NuGet\Cache*.nupkg /q
Full Package Clean
In most cases clearing the NuGet packages cache will suffice, sometimes you'll also need to manually delete other local packages caches
delete all NuGet packages in /packages folder:
rd /q /s packages
delete /bin and /obj folders in host project
rd /q /s bin obj
Versioning Scheme
All ServiceStack packages are published together in "lockstep" with the same version number so the effort to upgrade ServiceStack projects can be done all at same time, with low frequency.
ServiceStack Versions adopt the following 3-part versioning scheme:
{MAJOR}.{MINOR}.{PATCH}
Major versions
The {MAJOR} is reserved for Major releases like v5 containing structural changes that may require changes to external environment and/or project configurations and support for different .NET Runtimes:
v5.*- Support for .NET 5.0 and .NET Framework v4.5v6.*- Support for .NET 6.0 and .NET Framework v4.7.2v8.*- Support for .NET 8.0 and .NET Framework v4.7.2v10.*- Support for .NET 10.0 and .NET Framework v4.7.2
Minor versions
The {MINOR} version is used for major ServiceStack official releases which will have a {PATCH} version of 0.
Patch versions
The {PATCH} version is used to distinguish updates from normal releases where a {PATCH} above 0 indicates an Enhancement Release.
Whilst we want to minimize the effort for Customers to upgrade we also want to make any fixes or enhancements to the previous release available sooner as there are often fixes reported and resolved immediately after each release and made available in our pre-release NuGet packages feed that most Customers wont get until the next major Release on NuGet.
To deliver updates sooner we dedicate time immediately after each release to resolving issues and adding enhancements to existing features so we can publish update releases before starting work on new major features. Update releases will be primarily additive and minimally disruptive so they're safe to upgrade.
- An even
{PATCH}version number indicates an "Update" release published to NuGet. - An odd version number indicates a "pre-release" version that's only available on Feedz.io or GitHub Packages
Versioning scheme example:
- v5.0.0 - Current Major Release with structural changes
- v5.0.2 - Enhancement of Major v5.0.0 Release
- v5.0.3 - Pre-release packages published to MyGet only
- v5.0.4? - Enhancement of Major v5.0.0 Release (if any)
- v5.1.0 - Next Major Release
- v5.1.1 - Pre-release packages published to MyGet only
- v5.1.2? - Enhancement of Major v5.1.0 Release (if any)
- ...
- v6.0.0 - Next Major Release with structural changes