Our web (x and app) .NET Core tools are a versatile invaluable companion for all ServiceStack developers where it's
jam packed with functionality to power a number of exciting scenarios where it serves as a Sharp App
delivery platform where they can be run as a .NET Core Windows Desktop App with app or as a cross-platform Web App launcher
using web and we've already how it's now a #Script runner with web run and into a
Live #Script playground with web watch.
They also contain all features from our @servicestack/cli npm tools so you'll no longer need npm to create ServiceStack projects or Add/Update ServiceStack References.
To access available features, install with:
$ dotnet tool install --global web
Or if you had a previous version installed, update with:
$ dotnet tool update -g web
The Windows-only
apptool has better integration with Windows that can power .NET Core Windows Desktop Apps.
If you have .NET 10.0 LTS installed use the x dotnet tool:
$ dotnet tool install --global x
All
web,xandapphave equivalent base functionality, whilstapphas superset features for richer Windows integration
Usage
Then run web without any arguments to view Usage:
$ web
Usage:
web new List available Project Templates
web new <template> <name> Create New Project From Template
web <lang> Update all ServiceStack References in directory (recursive)
web <file> Update existing ServiceStack Reference (e.g. dtos.cs)
web <lang> <url> <file> Add ServiceStack Reference and save to file name
web csharp <url> Add C# ServiceStack Reference (Alias 'cs')
web typescript <url> Add TypeScript ServiceStack Reference (Alias 'ts')
web swift <url> Add Swift ServiceStack Reference (Alias 'sw')
web java <url> Add Java ServiceStack Reference (Alias 'ja')
web kotlin <url> Add Kotlin ServiceStack Reference (Alias 'kt')
web dart <url> Add Dart ServiceStack Reference (Alias 'da')
web fsharp <url> Add F# ServiceStack Reference (Alias 'fs')
web vbnet <url> Add VB.NET ServiceStack Reference (Alias 'vb')
web tsd <url> Add TypeScript Definition ServiceStack Reference
web proto <url> Add gRPC .proto ServiceStack Reference
web proto <url> <name> Add gRPC .proto and save to <name>.services.proto
web proto Update all gRPC *.services.proto ServiceStack References
web proto-langs Display list of gRPC supported languages
web proto-<lang> <url> Add gRPC .proto and generate language (-out <dir>)
web proto-<lang> <file|dir> Update gRPC .proto and re-gen language (-out <dir>)
web proto-<lang> Update all gRPC .proto's and re-gen lang (-out <dir>)
web mix Show available gists to mixin (Alias '+')
web mix <name> Write gist files locally, e.g: (Alias +init)
web mix init Create empty .NET Core ServiceStack App
web mix [tag] Search available gists
web mix <gist-url> Write all Gist text files to current directory
web gist <gist-id> Write all Gist text files to current directory
web run <name>.ss Run #Script within context of AppHost (or <name>.html)
web watch <name>.ss Watch #Script within context of AppHost (or <name>.html)
Language File Extensions:
.ss - #Script source file
.sc - #Script `code` source file
.l - #Script `lisp` source file
web lisp Start Lisp REPL
web open List of available Sharp Apps
web open <app> Install and run Sharp App
web run Run Sharp App in current directory
web run <name> Run Installed Sharp App
web run path/app.settings Run Sharp App at directory containing specified app.settings
web install List available Sharp Apps to install (Alias 'l')
web install <app> Install Sharp App (Alias 'i')
web uninstall List Installed Sharp Apps
web uninstall <app> Uninstall Sharp App
web publish Publish Sharp App to Gist (requires token)
web shortcut Create Shortcut for Sharp App
web shortcut <name>.dll Create Shortcut for .NET Core App
web get <url> Download remote file (-out <file|dir>)
dotnet tool update -g web Update to latest version
Options:
-h, --help, ? Print this message
-v, --version Print this version
-d, --debug Run in Debug mode for Development
-r, --release Run in Release mode for Production
-s, --source Change GitHub Source for App Directory
-f, --force Quiet mode, always approve, never prompt
--token Use GitHub Auth Token
--clean Delete downloaded caches
--verbose Display verbose logging
--ignore-ssl-errors Ignore SSL Errors
Add/Update ServiceStack References
This shows us we can Add a ServiceStack Reference with web <lang> <baseurl> which will let us create a TypeScript Reference
to the new Blazor Vue App using its ts file extension alias:
$ web ts https://blazor-vue.web-templates.io
Saved to: dtos.ts
Or create a C# ServiceStack Reference with:
$ web cs https://blazor-vue.web-templates.io
Saved to: dtos.cs
To update run web <lang> which will recursively update all existing ServiceStack References:
$ web ts
Updated: dtos.ts
Integrate with Visual Studio
You can also easily integrate this within your VS.NET dev workflows by adding it as an External Tool in the External Tools dialog box by choosing Tools > External Tools:
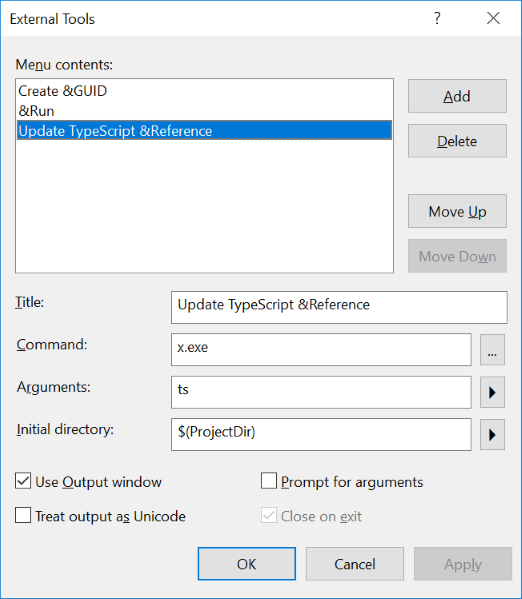
| Title | Update TypeScript &Reference |
| Command | web.exe |
| Arguments | ts |
| Initial directory | $(ProjectDir) |
Which will then let you update all your *dtos.ts TypeScript References in your project by clicking on Tools > Update TypeScript Reference
or using the ALT+T R keyboard shortcut.
If you wanted to Update your *dtos.cs C# ServiceStack References instead, just change Arguments to cs:
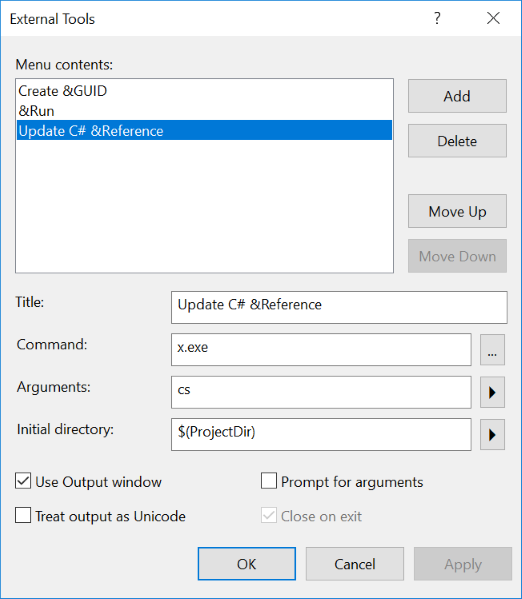
| Title | Update C# &Reference |
| Command | web.exe |
| Arguments | cs |
| Initial directory | $(ProjectDir) |
Refer to the web usage output above for the arguments or aliases for all other supported languages.
Integrate with Rider
Just like with VS.NET above you can add an External Tool
in JetBrains Rider by opening the Settings dialog with CTRL+ALT+S then searching for external tools
under the Tools category:
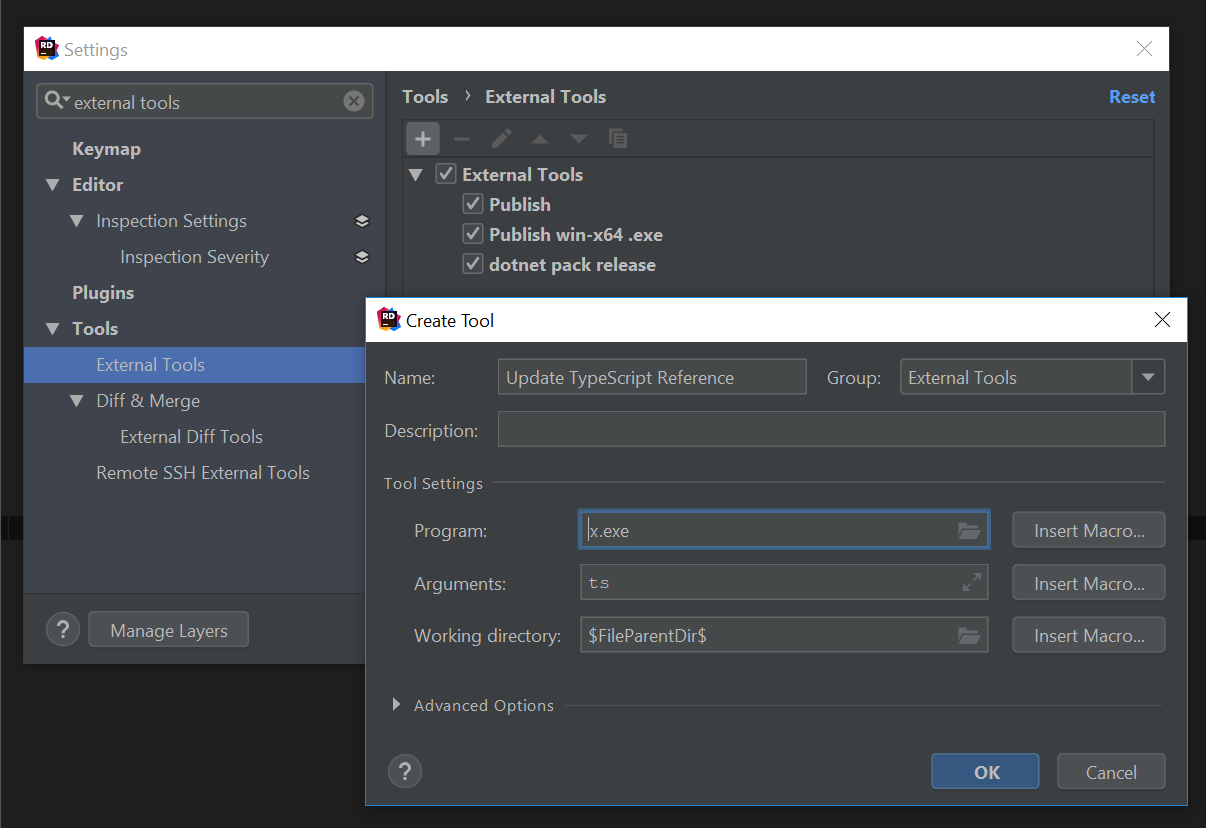
| Name | Update TypeScript Reference |
| Command | web.exe |
| Arguments | ts |
| Working directory | \(FileParentDir\) |
Now you can update your *dtos.ts TypeScript References in your project by clicking on External Tools > Update TypeScript Reference
in the right-click context menu:
If you're updating references frequently you can save time by assigning it a keyboard shortcut.
Create new Project Templates
See web new for available Project Templates you can create with:
$ web new
Mix Features into existing ASP.NET Core Apps
The web dotnet tool is a versatile utility belt packed with a number of features to simplify discovering, installing, running and deploying
.NET Core Apps. You can view the full list of supported commands by running web ?, e.g. another useful command is using web mix
for generating pre-set templates:
web mix Show available gists to mixin (Alias '+')
web mix <name> Write gist files locally, e.g: (Alias +init)
web mix init Create empty .NET Core ServiceStack App
web mix [tag] Search available gists
web gist <gist-id> Write all Gist text files to current directory
View available gists with:
$ web mix
Where you can use web mix nginx to generate a common nginx template configuration for reverse proxying .NET Core Apps, making configuring
Linux deployment servers for your .NET Core Apps less tedious.
In addition to the pre-set templates, you can create your own public GitHub gist with any number of different files customized for your Environment that anyone can write to their current directory with the gist id or gist URL:
$ web gist <gist-id>
Lisp REPL
Lisp's dynamism and extensibility makes it particularly well suited for explanatory programming whose access via a REPL is available
web and app dotnet tools.
The quick demo below shows the kind of exploratory programming available where you can query the scriptMethods available,
query an objects props, query the Lisp interpreter's global symbols table containing all its global state including all
defined lisp functions, macros and variables:
YouTube: youtu.be/RR7yk6ReNnQ
Annotated REPL Walk through
Here's an annotated version of the demo below which explains what each of the different expressions is doing.
Just like Sharp Scripts and Sharp Apps the Lisp REPL runs within the #Script Pages ScriptContext sandbox that when run from a Sharp App folder, starts a .NET Core App Server that simulates a fully configured .NET Core App. In this case it's running in the redis Sharp App directory where it was able to access its static web assets as well as its redis-server connection configured in its app.settings.
; quick lisp test!
(+ 1 2 3)
; List of ScriptMethodInfo that the ScriptContext running this Lisp Interpreter has access to
scriptMethods
; first script method
(:0 scriptMethods)
; show public properties of ScriptMethodInfo
(props (:0 scriptMethods))
; show 1 property per line
(joinln (props (:0 scriptMethods)))
; show both Property Type and Name
(joinln (propTypes (:0 scriptMethods)))
; view the Names of all avaialble script methods
(joinln (map .Name scriptMethods))
; view all script methods starting with 'a'
(globln "a*" (map .Name scriptMethods))
; view all script methods starting with 'env'
(globln "env*" (map .Name scriptMethods))
; print environment info about this machine seperated by spaces
(printlns envOSVersion envMachineName envFrameworkDescription envLogicalDrives)
; expand logical drives
(printlns envOSVersion envMachineName envFrameworkDescription "- drives:" (join envLogicalDrives " "))
; view all current global symbols defined in this Lisp interpreter
symbols
; view all symbols starting with 'c'
(globln "c*" symbols)
; see how many symbols are defined in this interpreter
(count symbols)
; see how many script methods there are available
(count scriptMethods)
; view the method signature for all script methods starting with 'all'
(globln "all*" (map .Signature scriptMethods))
; count all files accessible from the configured ScriptContext
(count allFiles)
; view the public properties of the first IVirtualFile
(props (:0 allFiles))
; display the VirtualPath of all available files
(joinln (map .VirtualPath allFiles))
; display the method signature for all script methods starting with 'findFiles'
(globln "findFiles*" (map .Signature scriptMethods))
; see how many .html files are available to this App
(count (findFiles "*.html"))
; see how many .js files are available to this App
(count (findFiles "*.js"))
; show the VirtualPath of all .html files
(joinln (map .VirtualPath (findFiles "*.html")))
; view the VirtualPath's of the 1st and 2nd .html files
(:0 (map .VirtualPath (findFiles "*.html")))
(:1 (map .VirtualPath (findFiles "*.html")))
; view the text file contents of the 1st and 2nd .html files
(fileTextContents (:0 (map .VirtualPath (findFiles "*.html"))))
(fileTextContents (:1 (map .VirtualPath (findFiles "*.html"))))
; display the method signatures of all script methods starting with 'redis'
(globln "redis*" (map .Signature scriptMethods))
; search for all Redis Keys starting with 'urn:' in the redis-server instances this App is configured with
(redisSearchKeys "urn:*")
; display the first redis search entry
(:0 (redisSearchKeys "urn:*"))
; display the key names of all redis keys starting with 'urn:'
(joinln (map :id (redisSearchKeys "urn:*")))
; find out the redis-server data type of the 'urn:tags' key
(redisCall "TYPE urn:tags")
; view all tags in the 'urn:tags' sorted set
(redisCall "ZRANGE urn:tags 0 -1")
; view the string contents of the 'urn:question:1' key
(redisCall "GET urn:question:1")
; parse the json contents of question 1 and display its tag names
(:Tags (parseJson (redisCall "GET urn:question:1")))
; extract the 2nd tag of question 1
(:1 (:Tags (parseJson (redisCall "GET urn:question:1"))))
; clear the Console screen
clear
; exit the Lisp REPL
quit
Enable features and access resources with app.settings
You can configure the Lisp REPL with any of the resources and features that Sharp Apps and
Gist Desktop Apps have access to, by creating a plain text app.settings file with all the
features and resources you want the Lisp REPL to have access to, e.g. this Pure Cloud App app.settings
allows the Lisp REPL to use Database Scripts against a AWS PostgreSQL RDS server and query remote
S3 Virtual Files using Virtual File System APIs:
# Note: values prefixed with '$' are resolved from Environment Variables
name AWS S3 PostgreSQL Web App
db postgres
db.connection $AWS_RDS_POSTGRES
files s3
files.config {AccessKey:$AWS_S3_ACCESS_KEY,SecretKey:$AWS_S3_SECRET_KEY,Region:us-east-1,Bucket:rockwind}
See the plugins app.settings for examples of how to load and configure ServiceStack Plugins.