A significant amount of behavior, functionality and customization of APIs and DTOs can be achieved declaratively through C# Attributes by annotating C# API Types and Data Models with the extensive functionality available in ServiceStack's Attributes.
This declarative expressiveness also extends to UI Attributes that can customize the behavior and appearance of Form UIs and formatted tabular resultsets, whose customizations are reused across all ServiceStack Auto UIs and Component libraries, including:
A great way to get a quick overview of what annotated DTOs looks like in practice is to browse the DTOs of Locode's Demos which uses declarative attributes extensively to achieve its customized behavior where you'll be able to test the cause & effect of different attributes against their Live Demos or by downloading and running a locally modified copy.
Talent Blazor - talent.locode.dev - download.zip
Talent Blazor is a good resource showing how to make use of Audit CRUD Events where every change is captured in an Executable Crud Audit Event Log and AutoApply Behaviors to change the behavior of Delete APIs to implement "Soft Deletes".
Chinook - chinook.locode.dev - download.zip
Chinook is a good simple Code-First example that's primarily focused on creating a customized UI in Locode.
Northwind Auto - northwind.locode.dev - download.zip
Whilst Northwind is a Database-First example, it still has access to the same attributes but are instead dynamically added at runtime.
Overview
Annotating APIs and Data Models is the primary way of enlisting existing functionality in ServiceStack where most of the functionality can be broadly grouped into customizing how Data Models map to RDBMS tables and make use of RDBMS features, customizing API behavior and annotating & documenting APIs to customize their appearance in UIs.
Data Model Attributes
These Data Model attributes can be used to utilize RDBMS features & customize how Types are mapped to RDBMS Tables.
Table Data Model Attributes
These OrmLite attributes can be used to customize how C# Types configure & map to RDBMS Tables.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
[Alias] |
Map C# Type Name to an alternative RDBMS Table |
[PostCreateTable] |
Run Custom SQL immediately after RDBMS table is created |
[PostDropTable] |
Run Custom SQL immediately after RDBMS table is dropped |
[PreCreateTable] |
Run Custom SQL immediately before RDBMS table is created |
[PostDropTable] |
Run Custom SQL immediately before RDBMS table is dropped |
[Schema] |
Define which RDBMS Schema Data Model belongs to |
[UniqueConstraint] |
Define a unique multi column RDBMS column constraint |
Column Property Attributes
These OrmLite attributes are used to customize how C# Properties configure & map to RDBMS Columns.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
[Alias] |
Map C# Property Name to an alternative RDBMS Column name |
[AutoId] |
Auto populate Property with a unique RDBMS generated UUID if supported otherwise with a new C# GUID |
[AutoIncrement] |
Auto populate Primary Key Property with an RDBMS generated Auto Incrementing Integer |
[BelongTo] |
Populate property from ambiguous column name in the specified joined table type |
[CheckConstraint] |
Create an Composite RDBMS Index and optional Unique constraint |
[Compute] |
Define that a Property maps to a computed RDBMS column |
[Computed] |
Ignore calculated C# Property from being persisted in RDBMS Table |
[CustomField] |
Create RDBMS using Custom SQL Data Type |
[CustomSelect] |
Populate property with Custom SELECT expression |
[CustomInsert] |
Populate INSERT parameter with Custom SQL expression |
[CustomUpdate] |
Populate UPDATE parameter with Custom SQL expression |
[DecimalLength] |
Create RDBMS Column with specified decimal scale & precision |
[Default] |
Create RDBMS Column definition with specified default value |
[EnumAsChar] |
Save Enum value as single char in RDBMS column |
[EnumAsInt] |
Save Enum integer value in RDBMS column |
[ForeignKey] |
Define an RDBMS Foreign Key Relationship |
[Ignore] |
Ignore property from consideration as an RDBMS column |
[IgnoreOnUpdate] |
Ignore this property in UPDATE statements |
[IgnoreOnInsert] |
Ignore this property in INSERT statements |
[Index] |
Create an RDBMS Column Index |
[PrimaryKey] |
Treat this property is the Primary Key of the table |
[Reference] |
Define this property as containing a foreign POCO Complex Type Reference |
[ReferenceField] |
Populate with a field from a foreign table in AutoQuery and Load* APIs |
[References] |
Document a reference to an external Type, used to create simple Foreign Key references |
[Required] |
Create NOT NULL Column Definitions in RDBMS Create Table statements |
[ReturnOnInsert] |
Indicate property should be included in returning/output clause of SQL INSERT Statements |
[RowVersion] |
Treat property as an automatically incremented RDBMS Row Version |
[StringLength] |
Define the RDBMS Column Definition variable character length |
[Unique] |
Define a unique RDBMS column constraint |
In addition to these generic Data Model attributes that work with any supported RDBMS, there are also PostgreSQL-specific and SQL Server specific attributes to unlock their respective RDBMS-specific features.
API Attributes
Use the Attributes to customize the functionality, behavior & accessibility of your APIs, and they're available endpoints.
Custom Serialization
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
[DataContract] |
Define Type as DTO Type and change serialization to opt-in [DataMember] properties |
[DataMember] |
Include property in Serialization and optionally change serializable Name and Order |
[Flags] |
Serialize an Enum's integer value instead |
[IgnoreDataMember] |
Ignore property from serialization |
Generic API Behavior
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
[Exclude] |
Instruct which APIs should be excluded from metadata & specified endpoints |
[Route] |
Make this API available on the specified user-defined route |
[Restrict] |
Restrict the accessibility of a service and its visibility in Metadata services |
[UploadTo] |
Specify which File Upload location should be used to manage these file uploads |
More information on usage of these attributes can be found in Routing Docs, Restricting Services and Managed File Uploads Docs.
AutoQuery Attributes
These attributes can be used to customize the querying behavior of AutoQuery APIs.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
[QueryDb] |
Change the default querying behaviour of AutoQuery filter properties |
[QueryDbField] |
Define field to use a custom AutoQuery filter |
AutoQuery CRUD Attributes
Use these attributes to customize the behavior of AutoQuery CRUD APIs.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
[AutoApply] |
Apply built-in composite generic behavior |
[AutoPopulate] |
Populate data models with generic user & system info |
[AutoFilter] |
Apply additional pre-configured filters to AutoQuery APIs |
[AutoMap] |
Map System Input properties to Data Model fields |
[AutoDefault] |
Specify to fallback default values when not provided |
[AutoIgnore] |
Ignore mapping Request DTO property to Data Model |
[AutoUpdate] |
Change the update behavior to only update non-default values |
Type Validation Attributes
As AutoQuery APIs typically don't have a Service implementation, the recommended way to protect access to them is to use the declarative Type Validators below as they're decoupled from any implementation and can be safely annotated on Request DTOs without requiring any implementation dependencies.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
[ValidateRequest] |
Validate Type against a custom Validator expression |
[ValidateIsAuthenticated] |
Protect access to this API to Authenticated Users only |
[ValidateIsAdmin] |
Protect access to this API to Admin Users only |
[ValidateHasPermission] |
Protect access to this API to only Users assigned with ALL Permissions |
[ValidateHasRole] |
Protect access to this API to only Users assigned with ALL Roles |
[ValidateApiKey] |
Protect access to this API to only Users with a valid API Key |
Property Validation Attributes
The Declarative Validation attributes enable an alternative way of defining Fluent Validation rules on properties.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
[Validate] |
Validate property against custom Validator expression |
[ValidateCreditCard] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation CreditCardValidator |
[ValidateEmail] |
Validate property against Fluent's AspNetCoreCompatibleEmailValidator |
[ValidateEmpty] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation EmptyValidator |
[ValidateEqual] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation EqualValidator |
[ValidateExactLength] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation ExactLengthValidator |
[ValidateExclusiveBetween] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation ExclusiveBetweenValidator |
[ValidateGreaterThan] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation GreaterThanValidator |
[ValidateGreaterThanOrEqual] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation GreaterThanOrEqualValidator |
[ValidateInclusiveBetween] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation InclusiveBetweenValidator |
[ValidateLength] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation LengthValidator |
[ValidateLessThan] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation LessThanValidator |
[ValidateLessThanOrEqual] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation LessThanOrEqualValidator |
[ValidateMaximumLength] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation MaximumLengthValidator |
[ValidateMinimumLength] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation MinimumLengthValidator |
[ValidateNotEmpty] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation NotEmptyValidator |
[ValidateNotEqual] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation NotEqualValidator |
[ValidateNotNull] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation NotNullValidator |
[ValidateNull] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation NullValidator |
[ValidateRegularExpression] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation RegularExpressionValidator |
[ValidateScalePrecision] |
Validate property against Fluent Validation ScalePrecisionValidator |
Authentication & Authorization Restrictions
These Request Filter Attributes applied to Service Implementation classes apply to all Service method implementations contained within them.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
[Authenticate] |
Protect access to this API to Authenticated Users only |
[RequiredClaim] |
Protect access to this API to only Authenticated Users with specified Claim |
[RequiredPermission] |
Protect access to this API to only Authenticated Users assigned with ALL Permissions |
[RequiredRole] |
Protect access to this API to only Authenticated Users assigned with ALL Roles |
[RequiresAnyPermission] |
Protect access to this API to Authenticated Users assigned with ANY Permissions |
[RequiresAnyRole] |
Protect access to this API to Authenticated Users assigned with ANY Roles |
Refer to Authentication Attribute docs for more info.
UI & Metadata Attributes
These attributes can be used to document and annotate APIs which will customize how they're documented and appear in Metadata services, Add ServiceStack Reference generated DTOs and metadata driven, capability-based Auto UIs like API Explorer, Locode and Swagger UI.
Annotate APIs
Whilst they can change how they appear and are accessed by external clients, it's important to note that they do not have any impact on the behavior & functionality of back-end APIs, i.e. your preferred validation method is still required in order to enforce validation.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
[Api] |
Document a short description for an API Type |
[ApiMember] |
Document a short description for an API Property |
[ApiResponse] |
Document potential API Responses this API could return |
[ApiAllowableValues] |
Document the allowable values for an API Property |
[Description] |
Annotate any Type, Property or Enum with a textual description |
[ExcludeMetadata] |
Exclude API from all Metadata Services |
[Id] |
Uniquely identify C# Types and properties with a unique integer in gRPC Services |
[Meta] |
Decorate any type or property with custom metadata |
[Meta] |
Decorate any type or property with custom metadata |
[Range] |
Document the allowable min and max range for this property |
[Required] |
Document that this is a required property |
[Notes] |
Document a longer form description about a Type |
Customize UI
These UI attributes can be used to customize Auto UI Form fields and how search results are rendered.
Result Formatters
Refer to the Formatters docs for more info on how to use formatters to customize search results.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
[Intl] |
Configure result field to use JavaScript's Intl formatter |
[IntlNumber] |
Configure result field to use JavaScript's Intl.NumberFormat formatter |
[IntlDateTime] |
Configure result field to use JavaScript's Intl.DateTimeFormat formatter |
[IntlRelativeTime] |
Configure result field to use JavaScript's Intl.RelativeTimeFormat formatter |
[Ref] |
Configure Lookup fields to use UI References to external Data Models |
Custom Fields and Inputs
These attributes can be used to customize how fields and HTML Input controls in Auto UIs like Locode and API Explorer.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
[Input] |
Customize the HTML Input control for a Property in Auto Form UIs |
[Field] |
Customize the HTML Input control and Form Field CSS for a Type's Property |
[FieldCss] |
Customize a Property Form Field CSS |
[ExplorerCss] |
Customize the Form and Field CSS in API Explorer |
[LocodeCss] |
Customize the Form and Field CSS in Locode |
We'll go through some examples to explore how they can be used to customize Locode and API Explorer UIs.
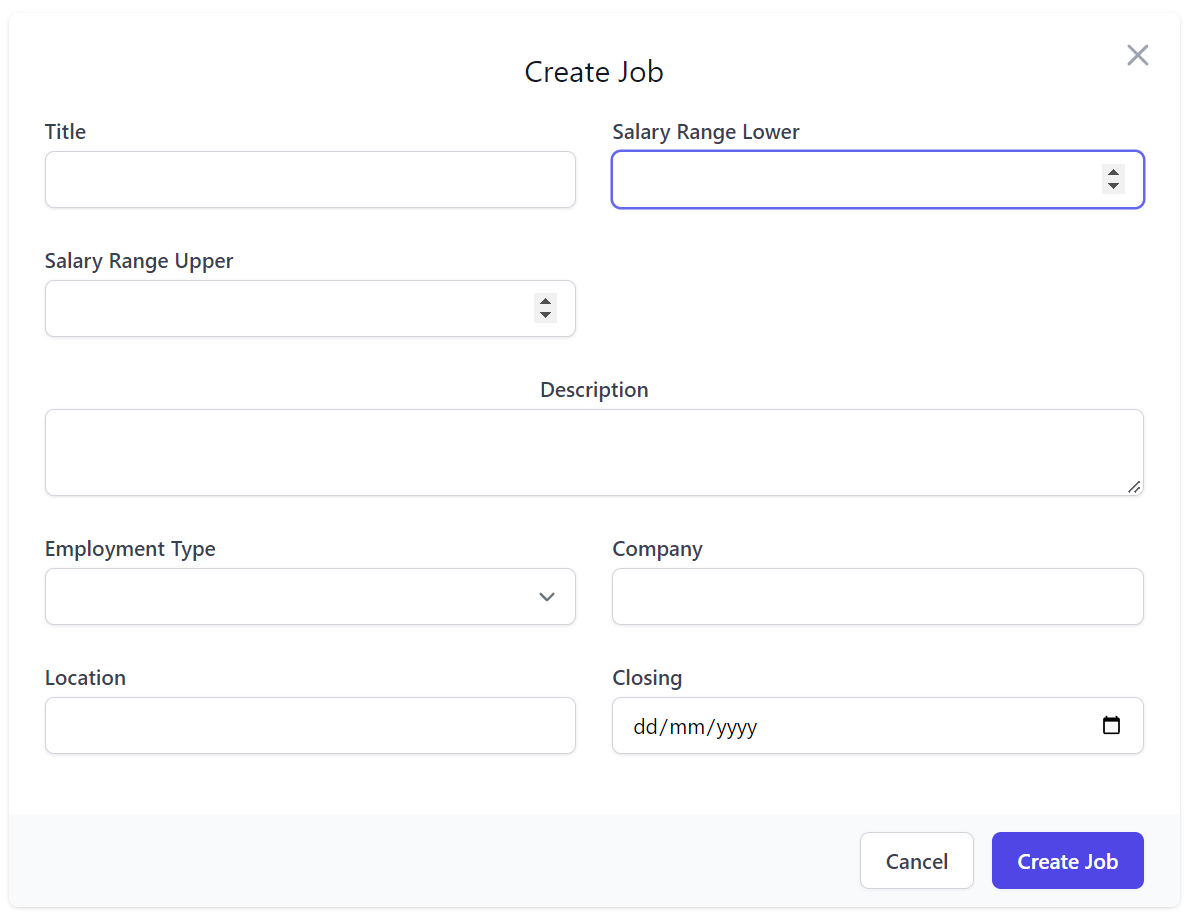
From the CreateJob Request DTO we can already see that Locode will use the most appropriate HTML Input for the specific
data type, e.g. a <input type=number> for integers, a <input type=date> for Date Types and a <select> dropdown
for properties with finite values like Enums.
We can also further customize each field with the [Input] attribute where we can change to use a <textarea> for
large text fields which we can pair with the [FieldCss] attribute to change the width of its encapsulating field
using TailwindCss Grid classes to change its width
and center its label:
public class CreateJob : ICreateDb<Job>, IReturn<Job>
{
public string Title { get; set; }
[ValidateGreaterThan(0)]
public int SalaryRangeLower { get; set; }
[ValidateGreaterThan(0)]
public int SalaryRangeUpper { get; set; }
[Input(Type = "textarea"), FieldCss(Field = "col-span-12 text-center")]
public string Description { get; set; }
public EmploymentType EmploymentType { get; set; }
public string Company { get; set; }
public string Location { get; set; }
public DateTime Closing { get; set; }
}
Which renders our preferred responsive form layout:
Field
The [Field] attribute is an alternative way to define both [Input] and [FieldCss] attributes on Types which
is especially useful when you don't have the property on the Request DTO you want to define because it's in a base class,
in which case you can use [Field] on the Request DTO:
[Field(nameof(Description), Type = "textarea", FieldCss="col-span-12 text-center")]
public class CreateJob : JobBase, ICreateDb<Job>, IReturn<Job> {}
Hiding Input Fields
Since the UIs only shows properties defined on Create and Update CRUD DTOs, not defining them will prevent them from
being included in the form. However, in the rare cases where you still want them defined on the Typed back-end API but
hidden from the UI, you can use Ignore=true:
public class UpdateJob : IPatchDb<Job>, IReturn<Job>
{
[Input(Ignore = true)]
public string Description { get; set; }
//...
}
[Field(nameof(Description), Ignore = true)]
public class UpdateJob : JobBase, IPatchDb<Job>, IReturn<Job> {}
This will completely exclude them from the UI, if you instead want them as an <input type=hidden> you can use:
[Input(Type="hidden")]
public string Description { get; set; }
Custom Form CSS
The high-level [LocodeCss] attribute can be used to change the entire Form layout instead where you'll be able to
change the default Form, FieldSet and Field CSS classes, e.g:
[LocodeCss(Field="col-span-12 sm:col-span-6", Fieldset = "grid grid-cols-6 gap-8",
Form = "border border-indigo-500 overflow-hidden max-w-screen-lg")]
[Field(nameof(BookingEndDate), LabelCss = "text-gray-800", InputCss = "bg-gray-100")]
[Field(nameof(Notes), Type = "textarea", FieldCss="col-span-12 text-center", InputCss = "bg-gray-100")]
public class UpdateBooking : IPatchDb<Booking>, IReturn<IdResponse>
{
public int Id { get; set; }
[ValidateNotNull]
public string? Name { get; set; }
public RoomType? RoomType { get; set; }
[ValidateGreaterThan(0)]
public int? RoomNumber { get; set; }
[ValidateGreaterThan(0), AllowReset]
public decimal? Cost { get; set; }
public DateTime? BookingStartDate { get; set; }
public DateTime? BookingEndDate { get; set; }
public string? Notes { get; set; }
public bool? Cancelled { get; set; }
}
Renders our custom Form layout:
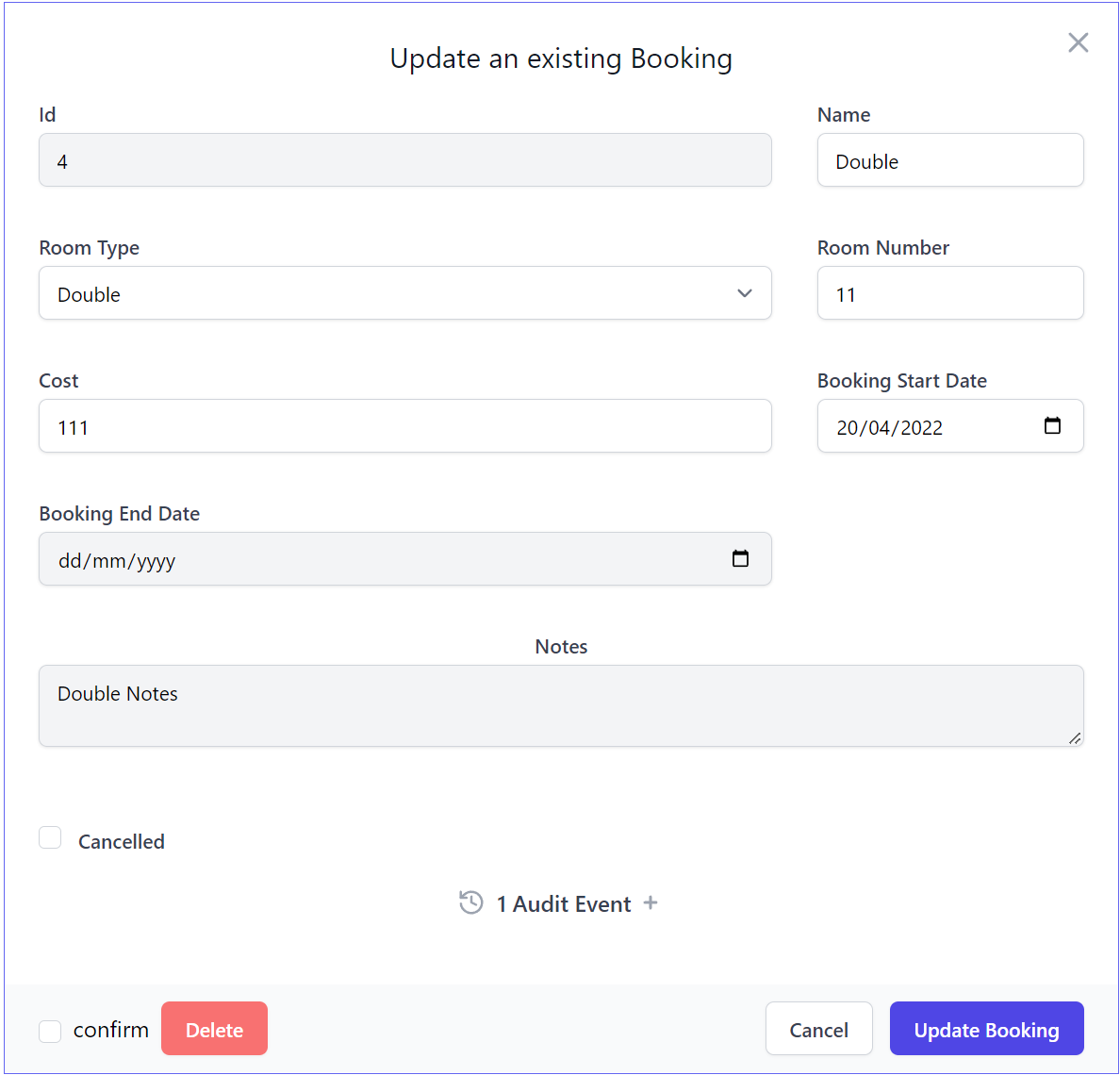
These changes only applies to the Form when viewed in Locode, to change the Form in API Explorer use [ExplorerCss]:
[ExplorerCss(Field="col-span-12 sm:col-span-6", Fieldset = "grid grid-cols-6 gap-8",
Form = "border border-indigo-500 overflow-hidden max-w-screen-lg")]
When more customization is needed checkout how you can replace the entire Form in the Custom Forms docs.