The Software world has an overload of contrasting and competing knowledge that it can be daunting to know how to develop software, what tools and patterns we should use, which technical literature we should follow and when and how we should adopt patterns. The overarching theme that has served us well over the years is a relentless pursuit for simplicity and seeking out the simplest solutions, with minimal abstractions, concepts that best solves any given problem.
Since its inception in 2008, this philosophy has helped ServiceStack become the worlds most versatile Services Framework - supporting an unparalleled number of Pluggable Formats, multitude of HTTP, SOAP and MQ Endpoints that can be hosted in a variety of hosting scenarios whilst providing a productive succinct, end-to-end Typed API for the most popular native Mobile and Desktop and .NET platforms. In the time other vendors have left a number of abandoned frameworks and failed HTTP abstractions behind for their next framework rewrite, ServiceStack has managed to stay lean, fast and continually enhance and evolve its single code-base to support every major HTTP Host delivered with .NET with an order of magnitude less resources. This is only achievable due to our relentness pursuit of simplicity, focus on underlying value, rewriting friction-encumbered providers whilst actively rejecting unnecessary complexity and abstractions and slow bloated technologies promoting well-known anti-patterns whose resulting value does not justify the level of investment and effort required to adopt it. We hope our experience can provide valuable insight and help with deciding what areas to focus on and which to avoid.
Software's biggest enemy
We consider Complexity and Large Code bases the single worst enemy of software development, and that along with meeting the project requirements and deriving value from our software, managing complexity and maintaining a minimal and low friction, evolvable code-base should be at the forefront of our minds as we're continually enhancing our software with new features and requirements. Any guidelines, rules or processes we add to increase software quality should be directly focused on managing its essential complexity. One of the best things we can do to reduce complexity is to reduce code-base size, i.e. DRYing repeatable code and eliminating any unnecessary abstractions, indirection, concepts, types and friction that isn't absolutely essential to the software's function.
In this light, YAGNI is one of the best principles to follow to ensure a simple and lean code-base by focusing on what's essential to delivering value.
Avoid blanket rules
We recommend avoiding "blanket rules" which we consider one of the primary causes of unnecessary complexity in Software, where it's often liberally and thoughtlessly applied, infecting a code-base without justification. Every time you impose an artificial limitation, you're creating friction and inertia to develop within its bounds in order to satisfy it, which is why any rule you enforce should be thoughtfully and carefully applied and limited to places where it adds value.
Be wary of invalid Rules and Patterns
Even Software Design Patterns are in many cases programming language deficiencies, where what's a useful in one language is unnecessary and more elegantly solved in more expressive and powerful languages. Likewise with "rules", what's a cautionary guideline in one domain may not be applicable in others. Therefore what's more important than "the rule" itself, is the value it actually provides and what concrete side-effect it's trying to prevent. Once we understand its true value, we can optimize to derive maximum value from it and together with YAGNI, know when to selectively apply it.
The Simple POCO Life
ServiceStack achieves a lot of its simplicity and reuse by being able to reuse the same POCOs indiscriminately anywhere to interface and freely communicate between its different libraries and components. This enables maximum value and reuse of your Models and reduces the friction in mapping between different domains which typically require having purpose-specific types, each with its own unique configuration limiting its applicability and potential re-use.
Heavy ORM models are poor DTOs
Not reusing data models as DTOs applies to Heavy ORM's which encourage Data Models with cyclical dependencies and proxied objects with tight coupling and embedded logic that can trigger unintended N+1 data access, making these models poor candidates for use as DTOs and why you should always copy them into purpose-specific DTOs that your Services can return so they're serializable without issue.
Clean POCOs
The complex Data Models stored in OrmLite or Redis doesn't suffer from any of these issues which are able to use clean, disconnected POCOs. They're loosely-coupled, where only the "Shape" of the POCO is significant, i.e. moving projects and changing namespaces won't impact serialization, how it's stored in RDBMS tables, Redis data structures, Caching providers, etc. You're also not coupled to specific types, you can use a different type to insert data in OrmLite than what you use to read from it, nor does it need to be the "exact Shape", as OrmLite can populate a DTO with only a subset of the fields available in the underlying table. There's also no distinction between Table, View or Stored procedure, OrmLite will happily map any result-set into any matching fields on the specified POCO, ignoring others.
Effectively this means POCOs in ServiceStack are extremely resilient and interoperable, so you can happily re-use the same DTOs in OrmLite and vice-versa without issue. If the DTO and Data models only deviate slightly, you can hide them from being serialized or stored in OrmLite with the attributes below:
public class Poco
{
[Ignore]
public int IgnoreInOrmLite { get; set; }
[IgnoreDataMember]
public int IgnoreInSerialization { get; set; }
}
Otherwise when you need to separate them, e.g. more fields were added to the RDBMS table than you want to
return, the DTO includes additional fields populated from alternative sources, or you just want your Services
to project them differently. At that point (YAGNI) you can take a copy of the DTO and add it to your Services
Implementation so they can grow separately, unimpeded by their different concerns.
You can then effortlessly convert between them using
ServiceStack's built-in Auto Mapping, e.g:
var dto = dbPoco.ConvertTo<Poco>();
INFO
The built-in Auto Mapping is also very tolerant and can co-erce properties with different types, e.g. to/from strings, different collection types, etc
Data Transfer Objects - DTOs
So if you're using clean, serializable POCOs without external dependencies (e.g. from OrmLite, Redis or alt
ServiceStack sources) you can happily re-use them as DTOs and freely refactor them out into different models
as-and-when you need to. But when you are re-using Data Models as DTOs they should still be maintained in the
ServiceModel project (aka DTO .dll) which should contain all the types that your Service returns.
DTOs should be logic and dependency-free so the only dependency the ServiceModel project references is the
impl-free ServiceStack.Interfaces.dll which as it's a .NET v4.5 and .NET Standard 2.0 .dll, can be freely referenced from all
.NET Mobile and Desktop platforms.
You want to ensure all types your Services return are in the DTO .dll since this, along with the base url of where your Services are hosted is all that's required for your Service Consumers to know in order to consume your Services. Which they can use with any of the .NET Service Clients to get an end-to-end Typed API without code-gen, tooling or any other artificial machinery. If clients prefer source code instead, they can use Add ServiceStack Reference to access the Servers typed DTOs in their preferred platform and language of choice.
Services
Services are the ultimate form of encapsulating complexity and offers the highest level of software reuse. They package its capabilities and makes them available remotely to your consumers with never any more complexity than the cost of a Service call. They're also a vital tool in managing the complexity of large systems which when modelled correctly are able to divide Monoliths into cohesive, reusable and composable functionality at a macro-level.
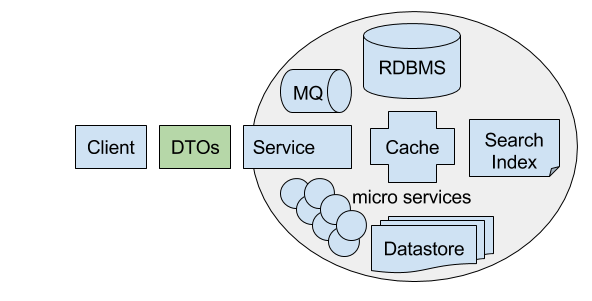
The DTOs are what defines your Services contract, keeping them isolated from any Server implementation is how your Service is able to encapsulate its capabilities (which can be of unbounded complexity) and make them available behind a remote facade. It separates what your Service provides from the complexity in how it realizes it. It defines the API for your Service and tells Service Consumers the minimum info they need to know to discover what functionality your Services provide and how to consume them (maintaining a similar role to Header files in C/C++ source code). Well-defined Service contracts decoupled from implementation, enforces interoperability ensuring that your Services don't mandate specific client implementations, ensuring they can be consumed by any HTTP Client on any platform. DTOs also define the shape and structure of your Services wire-format, ensuring they can be cleanly deserialized into native data structures, eliminating the effort in manually parsing Service Responses.
Parallel Client development
Since they capture the entire contract it also enables clients to develop their applications before the Services are implemented as they're able to bind their application to its concrete DTO models and can easily mock their Service client to return test data until the back-end Services are implemented.
As far as rules go, ensuring a well-defined Service Contract (DTOs) decoupled from its implementation goes to the very essence of what a Service is and the value it provides.
Request and Response DTOs
As for which DTOs make good candidates for re-use as Data Models, you don't want to use Request DTOs for anything other than defining your external Services API which is typically a Verb that's ideally grouped by Call Semantics and Response Types, e.g:
public class SearchProducts : IReturn<SearchProductsResponse>
{
public string Category { get; set; }
public decimal? PriceGreaterThan { get; set; }
}
Your RDBMS tables are normally entities defined as Nouns, i.e. what your Service returns:
public class SearchProductsResponse
{
public List<Product> Results { get; set; }
public ResponseStatus ResponseStatus { get; set; }
}
Even the containing Response DTO which defines what your Service returns isn't a good candidate for re-use as a Data Model. I'd typically use discrete DTOs for Service Responses as it allows freely extending existing Services to return extra data or metadata without breaking existing clients.
Other than the Request and Response DTOs, all other the Types that your Service returns would be candidates for re-use as Data Models, keeping them in the ServiceModel project for the reasons above.