Android Java-Lite protoc generated GrpcServiceClient Example
This Android gRPC Example differentiates from the Java gRPC Example by using the more appropriate Java Lite which results in a much smaller code size making it more suitable to be used on embedded Java platforms like Android.
In addition it uses the Android-compatible OK HTTP SSL Libraries in-place of Netty's SSL libraries and a
custom services.proto allow us to specify the Java package we want the generated gRPC client to use.
Install x dotnet tool:
dotnet tool install --global x
Create a new Android App with Android Studio:
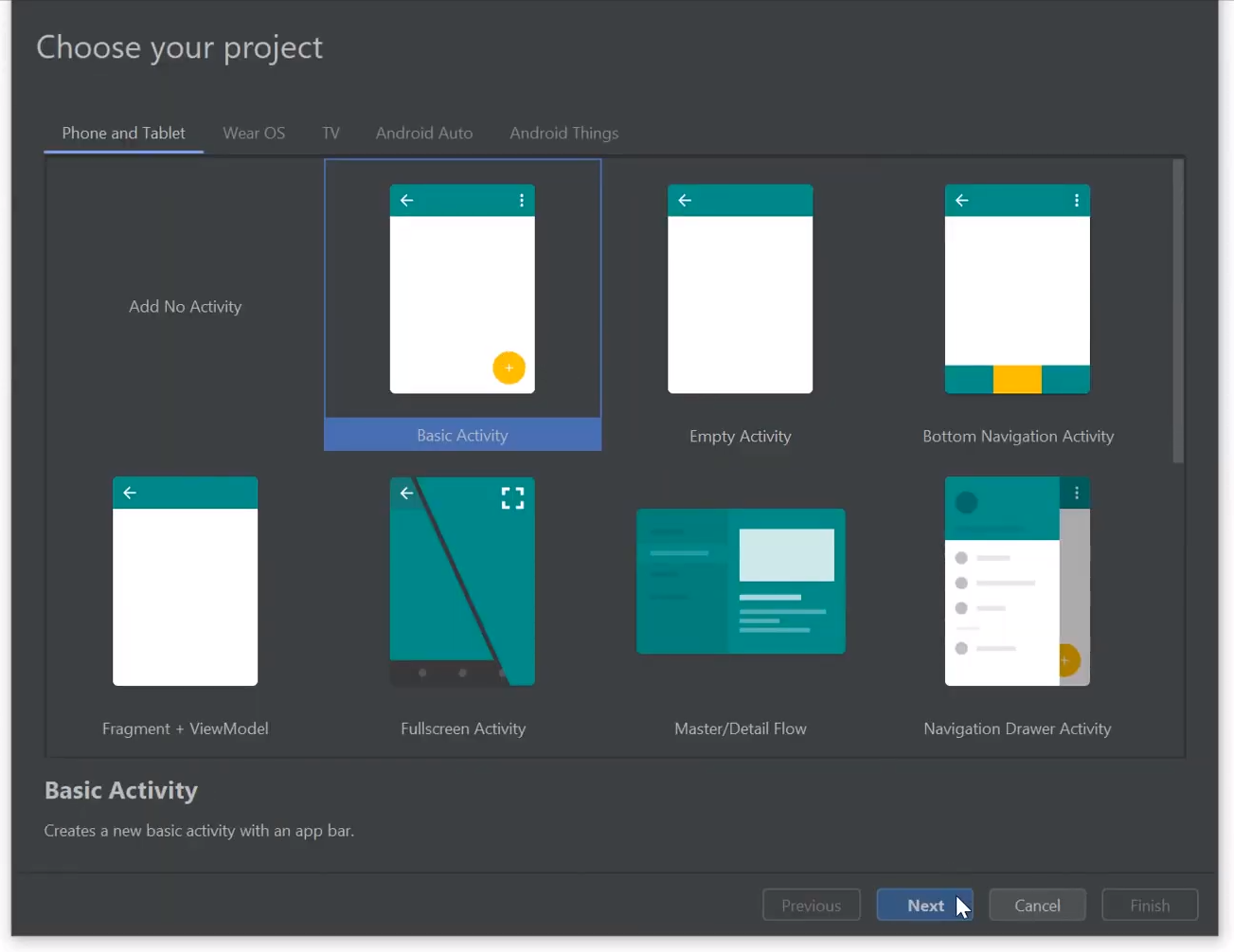 Add protoc generated TodoWorld DTOs and gRPC
Add protoc generated TodoWorld DTOs and gRPC GrpcServicesStub:
cd app\src\main\java
x proto-java https://todoworld.servicestack.net
Modify the downloaded services.proto to use the package name of your App, e.g:
option java_package = "net.servicestack.androidapp";
Generate a java-lite protoc gRPC client from your modified services.proto:
x proto-java-lite services.proto
Update build.gradle with required gRPC, protobuf and OK HTTP plugins and dependencies:
plugins {
id 'com.google.protobuf' version '0.8.8'
id 'idea'
}
//...
def grpcVersion = '1.27.0'
dependencies {
implementation 'javax.annotation:javax.annotation-api:1.2'
implementation "io.grpc:grpc-protobuf:${grpcVersion}"
implementation "io.grpc:grpc-auth:${grpcVersion}"
implementation "io.grpc:grpc-census:${grpcVersion}"
implementation "io.grpc:grpc-okhttp:${grpcVersion}"
implementation "io.grpc:grpc-stub:${grpcVersion}"
//...
}
Sync changes to your build.gradle to install the new dependencies:

Add the android.permission.INTERNET to your AndroidManifest.xml (before <application/> tag):
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
Use protoc generated DTOs and async GrpcServicesStub to perform non-blocking TodoWorld gRPC Service requests:
Android Java protoc gRPC insecure Example
ManagedChannel channel = ManagedChannelBuilder.forAddress(
"todoworld.servicestack.net", 50054).usePlaintext().build();
final GrpcServicesGrpc.GrpcServicesStub client =
GrpcServicesGrpc.newStub(channel);
fab.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
client.getHello(Services.Hello.newBuilder()
.setName("Android gRPC").build(),
new StreamObserver<Services.HelloResponse>() {
@Override
public void onNext(Services.HelloResponse value) {
Snackbar.make(view, value.getResult(), Snackbar.LENGTH_LONG)
.setAction("Action", null).show();
}
@Override public void onError(Throwable t) {}
@Override public void onCompleted() {}
});
});
Now run your App and click the Action button to make a plain-text gRPC Request:
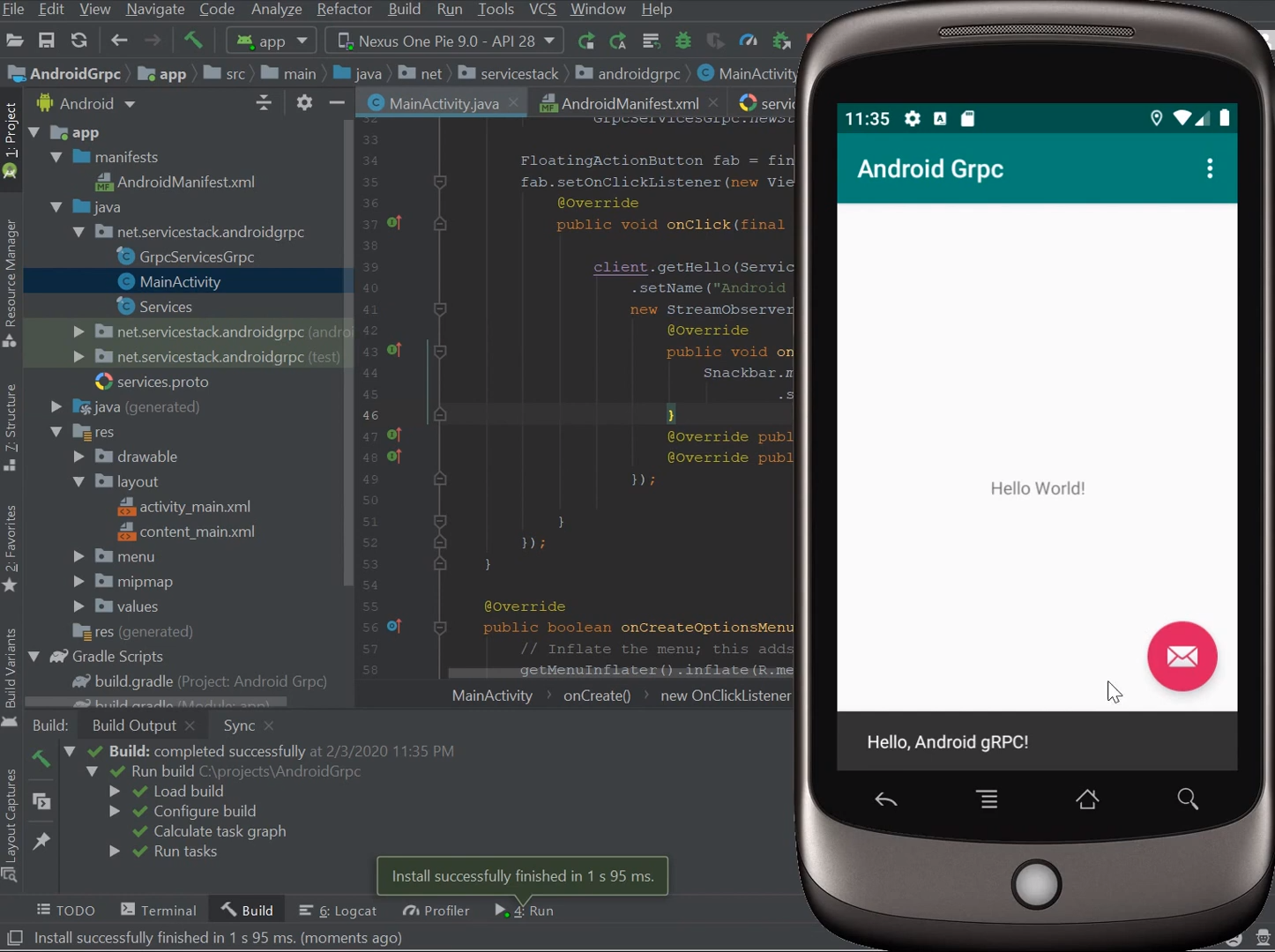
Android Java protoc gRPC SSL Example
To use gRPC SSL we'll need a copy of our gRPC's Service SSL Certificate which we can make available to our
Android App by saving it to our App's assets directory:
mkdir ..\assets
x get https://todoworld.servicestack.net/grpc.crt -out ../assets
Building an TLS Channel configured with a self-signed SSL Certificate requires a bit of effort with OK HTTP so we'll include a ChannelBuilder.java to wrap up the boiler plate:
npx add-in grpc-android
This simplifies the configuration required down to just the grpc.crt certificate loaded from the
App's Asset Manager, the host and port name of the gRPC SSL Channel:
ManagedChannel channel = null;
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = getResources().getAssets().open("grpc.crt");
channel = ChannelBuilder.buildTls(
"todoworld.servicestack.net", 50051, is);
is.close();
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Lets update the gRPC API call to reflect we're now using an SSL channel:
client.getHello(Services.Hello.newBuilder()
.setName("gRPC SSL").build(),
Now after re-running our App it'll perform gRPC SSL Service requests instead:
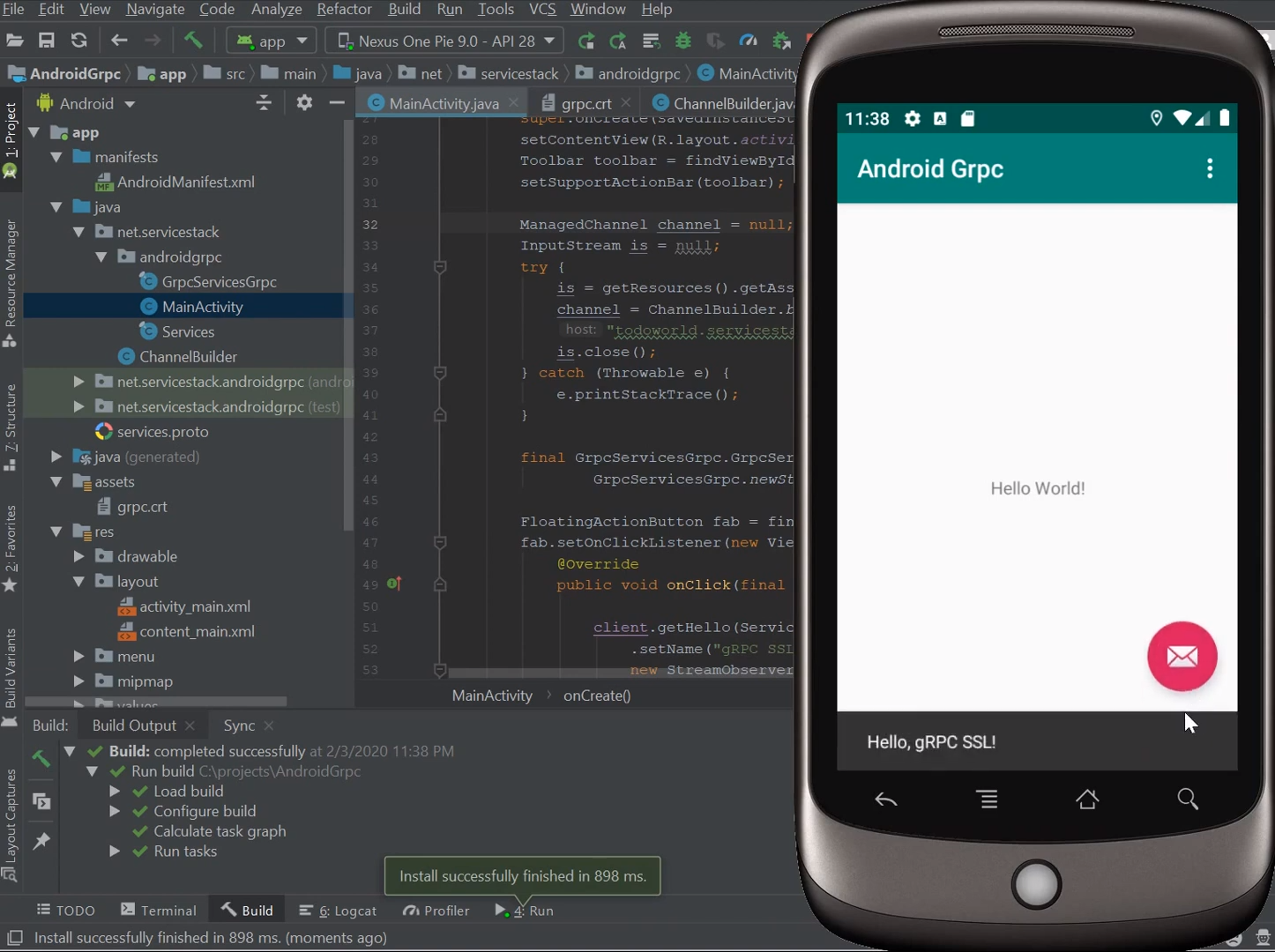
Refer to /mobile/java/AndroidGrpc for a complete example project.