TypeScript Data Models vs AutoGen
This approach starts by exporting your existing RDBMS schema to JSON, converting it into TypeScript Data Models, then generating the AutoQuery CRUD APIs, Data Models and DB migrations from those TypeScript definitions. By contrast, the AutoQuery AutoGen CRUD Services approach uses runtime C# reflection to inspect your DB schema and dynamically register AutoQuery CRUD Services for your tables at startup.
Generate CRUD APIs from TypeScript Data Models
A core feature of the okai tool is the ability to convert customizable TypeScript Data Models into C# AutoQuery CRUD APIs, RDBMS DataModel tables and DB Migrations.
This enables a flexible way to generate AutoQuery CRUD APIs for existing RDBMS tables, by:
- Exporting the existing RDBMS metadata to json
- Use
okaito convert the json metadata into TypeScript Data Models - Perform any customizations to the TypeScript Data Model as needed
- Use
okaito generate the AutoQuery CRUD APIs, RDBMS DataModel tables and DB Migrations
Why TypeScript?
Using TypeScript is an effortless way to define data models, offering a DSL-like minimal boilerplate format that's human-friendly to read and write which can leverage TypeScript's powerful Type System that's validated against the referenced api.d.ts schema to provide a rich authoring experience with strong typing and intellisense - containing all the C# Types, interfaces, and attributes used in defining APIs, DTOs and Data Models.
Blueprint for Code Generation
The TypeScript Data Models serve as the blueprint for generating everything needed to support the feature in your App, including the AutoQuery CRUD APIs, Admin UIs and DB Migrations that can re-create the necessary tables from scratch.
1. Generate RDBMS Metadata
The first step in generating TypeScript Data Models is to capture the metadata from the existing RDBMS tables which
we can do with the App.json AppTask below which uses your App's configured
RDBMS connection to generate the Table Definitions for all tables in the specified RDBMS connection and schema
to the file of your choice (e.g App_Data/App.json):
AppTasks.Register("App.json", args =>
appHost.VirtualFiles.WriteFile("App_Data/App.json",ClientConfig.ToSystemJson(
migrator.DbFactory.GetTables(namedConnection:null, schema:null))));
This task can then be run from the command line with:
dotnet run --AppTasks=App.json
Which generates App_Data/App.json containing the table definition metadata for all tables in
the specified RDBMS, e.g:
[
{
"name": "AspNetUserClaims",
"columns": [
{
"columnName": "Id",
"columnOrdinal": 0,
"columnSize": -1,
"numericPrecision": 0,
"numericScale": 0,
"isUnique": true,
"isKey": true,
"baseCatalogName": "techstacks",
"baseColumnName": "Id",
"baseSchemaName": "public",
"baseTableName": "AspNetUserClaims",
"dataType": "System.Int32",
"allowDBNull": false,
"providerType": 9,
"isAliased": false,
"isExpression": false,
"isAutoIncrement": true,
"isRowVersion": false,
"isHidden": false,
"isLong": false,
"isReadOnly": false,
"dataTypeName": "integer",
"columnDefinition": "INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT"
},
],
...
]
Different Connection or DB Schema
If you prefer to generate the metadata for a different connection or schema, you can create a new AppTask
with your preferred namedConnection and/or schema, e.g:
AppTasks.Register("Sales.json", args =>
appHost.VirtualFiles.WriteFile("Sales.json", ClientConfig.ToSystemJson(
migrator.DbFactory.GetTables(namedConnection:"reports",schema:"sales"))));
That you could then generate with:
dotnet run --AppTasks=Sales.json
2. Generate TypeScript Data Models
The next step is to generate TypeScript Data Models from the captured metadata which can be done with the okai tool
by running the convert command with the path to the App.json JSON table definitions which will generate the
TypeScript Data Models to stdout which can be redirected to a file in your ServiceModel project, e.g:
npx okai convert App_Data/App.json > ../MyApp.ServiceModel/App.d.ts
3. Generate CRUD APIs and Admin UIs
The data models defined in the App.d.ts TypeScript Declaration file is what drives the generation of the Data Models, APIs, DB Migrations and Admin UIs. This can be further customized by editing the TypeScript Declaration file and re-running the okai tool with just the filename, e.g:
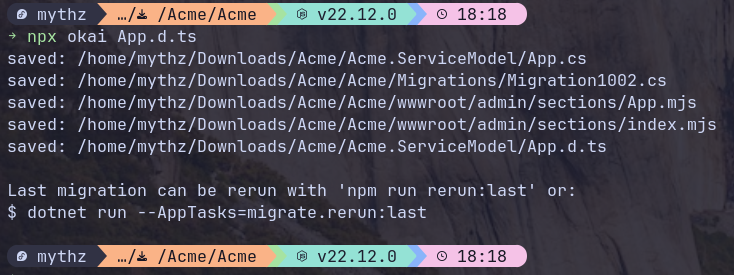
npx okai App.d.ts
Which will re-generate the Data Models, APIs, DB Migrations and Admin UIs based on the updated Data Models.
TIP
You only need to specify the App.d.ts TypeScript filename (i.e. not the filepath) from
anywhere within your .NET solution
Live Code Generation
If you'd prefer to see the generated code in real-time you can add the --watch flag to watch the
TypeScript Declaration file for changes and automatically re-generate the generated files on Save:
npx okai App.d.ts --watch